Maize Oxalyl-CoA Decarboxylase1 Degrades Oxalate and Affects the Seed Metabolome and Nutritional Quality
- PMID: 30201823
- PMCID: PMC6241262
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.18.00266
Maize Oxalyl-CoA Decarboxylase1 Degrades Oxalate and Affects the Seed Metabolome and Nutritional Quality
Abstract
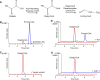
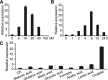
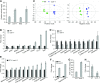
The organic acid oxalate occurs in microbes, animals, and plants; however, excessive oxalate accumulation in vivo is toxic to cell growth and decreases the nutritional quality of certain vegetables. However, the enzymes and functions required for oxalate degradation in plants remain largely unknown. Here, we report the cloning of a maize (Zea mays) opaque endosperm mutant that encodes oxalyl-CoA decarboxylase1 (EC4.1.1.8; OCD1). Ocd1 is generally expressed and is specifically induced by oxalate. The ocd1 mutant seeds contain a significantly higher level of oxalate than the wild type, indicating that the ocd1 mutants have a defect in oxalate catabolism. The maize classic mutant opaque7 (o7) was initially cloned for its high lysine trait, although the gene function was not understood until its homolog in Arabidopsis thaliana was found to encode an oxalyl-CoA synthetase (EC 6.2.1.8), which ligates oxalate and CoA to form oxalyl-CoA. Our enzymatic analysis showed that ZmOCD1 catalyzes oxalyl-CoA, the product of O7, into formyl-CoA and CO2 for degradation. Mutations in ocd1 caused dramatic alterations in the metabolome in the endosperm. Our findings demonstrate that ZmOCD1 acts downstream of O7 in oxalate degradation and affects endosperm development, the metabolome, and nutritional quality in maize seeds.
© 2018 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved.
Figures
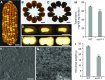
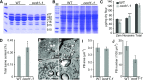

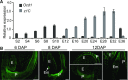
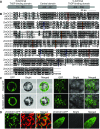

Comment in
-
Nutritious corn.Nat Plants. 2018 Oct;4(10):741. doi: 10.1038/s41477-018-0281-z. Nat Plants. 2018. PMID: 30287956 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bateman D.F., Beer S.V. (1965). Simultaneous production and synergistic action of oxalic acid and polygalacturonase during pathogenesis by Sclerotium rolfsii. Phytopathology 55: 204–211. - PubMed
-
- Berthold C.L., Moussatche P., Richards N.G., Lindqvist Y. (2005). Structural basis for activation of the thiamin diphosphate-dependent enzyme oxalyl-CoA decarboxylase by adenosine diphosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 280: 41645–41654. - PubMed
-
- Brzezicha-Cirocka J., Grembecka M., Szefer P. (2016). Oxalate, magnesium and calcium content in selected kinds of tea: impact on human health. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 242: 383–389.
-
- Casteels M., Sniekers M., Fraccascia P., Mannaerts G.P., Van Veldhoven P.P. (2007). The role of 2-hydroxyacyl-CoA lyase, a thiamin pyrophosphate-dependent enzyme, in the peroxisomal metabolism of 3-methyl-branched fatty acids and 2-hydroxy straight-chain fatty acids. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 35: 876–880. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

