Functional connectomics from neural dynamics: probabilistic graphical models for neuronal network of Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 30201841
- PMCID: PMC6158227
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0377
Functional connectomics from neural dynamics: probabilistic graphical models for neuronal network of Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
We propose an approach to represent neuronal network dynamics as a probabilistic graphical model (PGM). To construct the PGM, we collect time series of neuronal responses produced by the neuronal network and use singular value decomposition to obtain a low-dimensional projection of the time-series data. We then extract dominant patterns from the projections to get pairwise dependency information and create a graphical model for the full network. The outcome model is a functional connectome that captures how stimuli propagate through the network and thus represents causal dependencies between neurons and stimuli. We apply our methodology to a model of the Caenorhabditis elegans somatic nervous system to validate and show an example of our approach. The structure and dynamics of the C. elegans nervous system are well studied and a model that generates neuronal responses is available. The resulting PGM enables us to obtain and verify underlying neuronal pathways for known behavioural scenarios and detect possible pathways for novel scenarios.This article is part of a discussion meeting issue 'Connectome to behaviour: modelling C. elegans at cellular resolution'.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; functional connectome; neuronal networks; probabilistic graphical models.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures


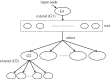

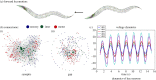


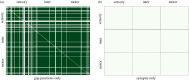
 sensory, motor
sensory, motor  motor, sensory
motor, sensory motor are zoomed in to compare detailed differences in gap, synaptic and PGM connections. Input neurons that activate the majority of the responding neurons are labelled.
motor are zoomed in to compare detailed differences in gap, synaptic and PGM connections. Input neurons that activate the majority of the responding neurons are labelled.

References
-
- Koller D, Friedman N, Getoor L, Taskar B. 2007. Graphical models in a nutshell. In Introduction to statistical relational learning, pp. 13–55. Cambridge, MA: MIT press.
-
- Koller D, Friedman N. 2009. Probabilistic graphical models: principles and techniques. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
-
- Murphy KP. 2012. Machine learning: a probabilistic perspective. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
-
- Kolar M, Song L, Ahmed A, Xing EP. 2010. Estimating time-varying networks. Ann. Appl. Stat. 4, 94–123. (10.1214/09-aoas308) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
