Are Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids the Link between the Immune System and the Microbiome towards Modulating Cancer?
- PMID: 30201858
- PMCID: PMC6163617
- DOI: 10.3390/medicines5030102
Are Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids the Link between the Immune System and the Microbiome towards Modulating Cancer?
Abstract
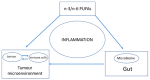
Three recent studies revealed synergy between immune-checkpoint inhibitors and the microbiome as a new approach in the treatment of cancer. Incidentally, there has been significant progress in understanding the role of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in modulating cancer and the immune system, as well as in regulating the microbiome. Inflammation seems to be the common denominator among these seemingly unrelated biological entities-immune system, the microbiome, and long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LC-PUFAs). This commentary presents a hypothesis proposing the existence of an optimal level of LC-PUFAs that nurtures the suitable gut microbiota preventing dysbiosis. This synergy between optimal LC-PUFAs and gut microbiota helps the immune system overcome the immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment including enhancing the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. A model on how LC-PUFAs (such as omega(n)-3 and n-6 fatty acids) forms a synergistic triad with the immune system and the microbiome in regulating inflammation to maintain homeostasis is presented. The principles underlying the hypothesis provide a basis in managing and even preventing cancer and other chronic diseases associated with inflammation.
Keywords: cancer; dysbiosis; gut health; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy; inflammation; microbiome; omega-3 fatty acids; omega-6 fatty acids; polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The author owns equity in Xerion Limited, which has an exclusive commercial license on the PUFA coat technology from the University of Adelaide—described in [39].
Figures
Similar articles
-
N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Gut Microbiota.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023;26(5):892-905. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666220701121025. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023. PMID: 35786331 Review.
-
Impact of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on the Gut Microbiota.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 7;18(12):2645. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122645. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29215589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associations among Dietary Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, the Gut Microbiota, and Intestinal Immunity.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Jan 2;2021:8879227. doi: 10.1155/2021/8879227. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 33488295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-term supplementation with ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids modulates primarily mucolytic species from the gut luminal mucin niche in a human fermentation system.Gut Microbes. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2120344. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2120344. Gut Microbes. 2022. PMID: 36109831 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular engineering strategies toward sustainable omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids production: State of the art and perspectives.Biotechnol Adv. 2020 May-Jun;40:107497. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.107497. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Biotechnol Adv. 2020. PMID: 31830520 Review.
Cited by
-
Marine unsaturated fatty acids: structures, bioactivities, biosynthesis and benefits.RSC Adv. 2019 Oct 31;9(61):35312-35327. doi: 10.1039/c9ra08119d. eCollection 2019 Oct 31. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35528072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Dietary and Supplemental Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Risk of Recurrent Gout Flares.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Sep;71(9):1580-1586. doi: 10.1002/art.40896. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30908893 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Checkpoint Blockade for Advanced NSCLC: A New Landscape for Elderly Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 7;20(9):2258. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092258. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31067796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Supplementation with Omega-6 LC-PUFA-Rich Microalgae Regulates Mucosal Immune Response and Promotes Microbial Diversity in the Zebrafish Gut.Biology (Basel). 2020 Jun 5;9(6):119. doi: 10.3390/biology9060119. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32517017 Free PMC article.
-
Omega-3PUFA Attenuates MNU-Induced Colorectal Cancer in Rats by Blocking PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2 Signaling.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Mar 5;13:1953-1965. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S241298. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32184629 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

