The Protective Effect of a Long-Acting and Multi-Target HM-3-Fc Fusion Protein in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 30201867
- PMCID: PMC6163367
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092683
The Protective Effect of a Long-Acting and Multi-Target HM-3-Fc Fusion Protein in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
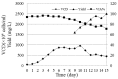
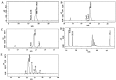
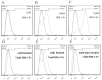
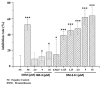
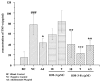
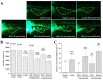
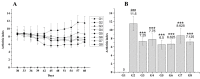
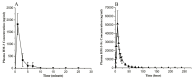
Current treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is limited by relative shortage of treatment targets. HM-3 is a novel anti-RA polypeptide consisting of 18 amino acids with integrin αVβ3 and α5β1 as targets. Previous studies confirmed that HM-3 effectively inhibited the synovial angiogenesis and the inflammatory response. However, due to its short half-life, the anti-RA activity was achieved by frequent administration. To extend the half-life of HM-3, we designed a fusion protein with name HM-3-Fc, by combination of modified Fc segment of immunoglobulin 4 (IgG4) with HM-3 polypeptide. In vitro cell experiments demonstrated that HM-3-Fc inhibited the proliferation of splenic lymphocytes and reduced the release of TNF-α from macrophages. The pharmacodynamics studies on mice paw in Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) model demonstrated that HM-3-Fc administered once in 5 days in the 50 and 25 mg/kg groups, or once in 7 days in the 25 mg/kg group showed a better protective effect within two weeks than the positive control adalimumab and HM-3 group. Preliminary pharmacokinetic studies in cynomolgus confirmed that the in vivo half-life of HM-3-Fc was 15.24 h in comparison with 1.32 min that of HM-3, which demonstrated that an Fc fusion can effectively increase the half-life of HM-3 and make it possible for further reduction of subcutaneous injection frequency. Fc-HM-3 is a long-acting active molecule for RA treatment.
Keywords: Fc-domain of immunoglobulin G4; HM-3; TNF-α; half-life; inflammatory response; pharmacodynamics; rheumatoid arthritis; synovial angiogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

