Iron Absorption in Iron-Deficient Women, Who Received 65 mg Fe with an Indonesian Breakfast, Is Much Better from NaFe(III)EDTA than from Fe(II)SO₄, with an Acceptable Increase of Plasma NTBI. A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 30201907
- PMCID: PMC6161297
- DOI: 10.3390/ph11030085
Iron Absorption in Iron-Deficient Women, Who Received 65 mg Fe with an Indonesian Breakfast, Is Much Better from NaFe(III)EDTA than from Fe(II)SO₄, with an Acceptable Increase of Plasma NTBI. A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
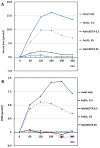
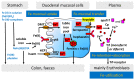
Plasma non-transferrin-bound iron (NTBI) is potentially harmful due to the generation of free radicals that cause tissue damage in vascular and other diseases. Studies in iron-replete and iron-deficient subjects, receiving a single oral test dose of Fe(II)SO₄ or NaFe(III)EDTA with water, revealed that FeSO₄ was well absorbed when compared with NaFeEDTA, while only the Fe(II) compound showed a remarkable increase of NTBI. As NaFeEDTA is successfully used for food fortification, a double-blind randomized cross-over trial was conducted in 11 healthy women with uncomplicated iron deficiency. All subjects received a placebo, 6.5 mg FeSO₄, 65 mg FeSO₄, 6.5 mg NaFeEDTA, and 65 mg NaFeEDTA with a traditional Indonesian breakfast in one-week intervals. Blood tests were carried out every 60 min for five hours. NTBI detection was performed using the fluorescein-labeled apotransferrin method. Plasma iron values were highly increased after 65 mg NaFeEDTA, twice as high as after FeSO₄. A similar pattern was seen for NTBI. After 6.5 mg of NaFeEDTA and FeSO₄, NTBI was hardly detectable. NaFeEDTA was highly effective for the treatment of iron deficiency if given with a meal, inhibiting the formation of nonabsorbable Fe-complexes, while NTBI did not exceed the range of normal values for iron-replete subjects.
Keywords: FeSO4; Indonesia; NaFeEDTA; developing countries; iron deficiency anemia; non-transferrin-bound iron (NTBI); nutrient iron; oral iron therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fortification iron as ferrous sulfate plus ascorbic acid is more rapidly absorbed than as sodium iron EDTA but neither increases serum nontransferrin-bound iron in women.J Nutr. 2011 May;141(5):822-7. doi: 10.3945/jn.110.136127. Epub 2011 Mar 23. J Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21430252 Clinical Trial.
-
The potential role of NaFeEDTA as an iron fortificant.Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2004 Nov;74(6):421-34. doi: 10.1024/0300-9831.74.6.421. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2004. PMID: 15743018 Review.
-
Oral administration of ferrous sulfate, but not of iron polymaltose or sodium iron ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (NaFeEDTA), results in a substantial increase of non-transferrin-bound iron in healthy iron-adequate men.Food Nutr Bull. 2012 Jun;33(2):128-36. doi: 10.1177/156482651203300206. Food Nutr Bull. 2012. PMID: 22908694 Clinical Trial.
-
Sodium iron EDTA [NaFe(III)EDTA] as a food fortificant does not influence absorption and urinary excretion of manganese in healthy adults.J Nutr. 1998 Jul;128(7):1139-43. doi: 10.1093/jn/128.7.1139. J Nutr. 1998. PMID: 9649597
-
Iron and malaria: absorption, efficacy and safety.Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2010 Oct;80(4-5):279-92. doi: 10.1024/0300-9831/a000035. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2010. PMID: 21462111 Review.
Cited by
-
Iron-fortified water: a new approach for reducing iron deficiency anemia in resource-constrained settings.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 21;13(1):13565. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40600-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37604937 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of an Acceptable Portion Size of Daal for a Bangladeshi Community-Based Iron Intervention in Adolescent Girls: A Feasibility Study.Nutrients. 2021 Mar 26;13(4):1080. doi: 10.3390/nu13041080. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33810220 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Administration of Bioavailable Curcumin Alongside Ferrous Sulphate Supplements Does Not Impair Iron Absorption in Healthy Adults in a Randomised Trial.Nutrients. 2021 Jul 3;13(7):2300. doi: 10.3390/nu13072300. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34371810 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Iron as Therapeutic Target in Human Diseases.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019 Dec 5;12(4):178. doi: 10.3390/ph12040178. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31817314 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Acute Serum Iron, Non-Transferrin-Bound Iron, and Gastrointestinal Symptoms with 3-Week Consumption of Iron-Enriched Aspergillus oryzae Compared with Ferrous Sulfate.Curr Dev Nutr. 2019 Nov 7;3(12):nzz127. doi: 10.1093/cdn/nzz127. eCollection 2019 Dec. Curr Dev Nutr. 2019. PMID: 32154497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kodyat B., Kosen S., de Pree S. Iron deficiency in Indonesia: Current situation and intervention. Nutr. Res. 1998;18:1953–1963. doi: 10.1016/S0271-5317(98)00165-1. - DOI
-
- Darmawan M.A., Karima N.N., Maulida N.N. Potential of Iron Fortification Complex Compounds against Soybean Food for Anemia Problem Solution in Indonesia. J. Adv. Agric. Technol. 2017;4:185–189. doi: 10.18178/joaat.4.2.185-189. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

