Quality Evaluation of Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex by Fingerprint⁻Chemical Pattern Recognition
- PMID: 30201911
- PMCID: PMC6225206
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23092307
Quality Evaluation of Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex by Fingerprint⁻Chemical Pattern Recognition
Abstract
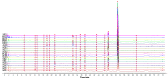
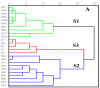
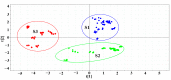
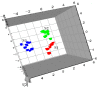
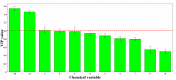
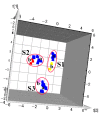
Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex (PCC) and Phellodendri Amurensis Cortex (PAC) are increasingly being used as traditional herbal medicines, but they are often mistaken for each other. In this study, the fingerprints of PCC from six different geographical sources were obtained by high-performance liquid chromatography, and multivariate chemometric methods were used for comprehensive analysis. Two unsupervised pattern recognition models (principal component analysis and hierarchical cluster analysis) and a supervised pattern recognition model (partial least squares discriminant analysis) were established on the basis of the chemical composition and physical traits of PCC and PAC. PCC and PAC were found to be distinguishable by these methods. The PCC category was divisible into two categories, one with more crude cork and a maximum thickness of ~1.5 mm, and the other with less net crude cork and a maximum thickness of 0.5 mm. According to the model established by partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA), the important chemical marker berberine hydrochloride was obtained and analyzed quantitatively. From these results combined with chemometric and content analyses, the preliminary classification standards for phellodendron were established as three grades: superior, first-order and mixed. Compared with the traditional identification methods of thin layer chromatography identification and microscopic identification, our method for quality evaluation is relatively simple. It provides a basis and reference for identification of PCC and enables establishment of grade standards. It also could be applied in quality control for compound preparations containing PCC.
Keywords: Phellodendri Amurensis Cortex (PAC); Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex (PCC); chemical pattern recognition; fingerprint; quality evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phellodendri Cortex: A Phytochemical, Pharmacological, and Pharmacokinetic Review.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Apr 1;2019:7621929. doi: 10.1155/2019/7621929. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31057654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Preparation and quality standard of standard decoction of Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex pieces].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018 Mar;43(5):873-878. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20180105.012. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29676081 Chinese.
-
Chemical fingerprint analysis of Phellodendri Amurensis Cortex by ultra performance LC/Q-TOF-MS methods combined with chemometrics.J Sep Sci. 2010 Nov;33(21):3347-53. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201000426. J Sep Sci. 2010. PMID: 21049522
-
Fingerprinting and simultaneous determination of alkaloids and limonins in Phellodendri amurensis cortex from different locations by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection.J Chromatogr Sci. 2015 Jan;53(1):161-6. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bmu034. Epub 2014 May 28. J Chromatogr Sci. 2015. PMID: 24872523
-
[Progress on chemical pattern recognition in traditional Chinese medicines by multidimensional information of metabolic fingerprinting analysis].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012 Apr;37(8):1081-8. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22779354 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Phellodendri Cortex: A Phytochemical, Pharmacological, and Pharmacokinetic Review.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Apr 1;2019:7621929. doi: 10.1155/2019/7621929. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31057654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A strategy for qualitative and quantitative profiling of glycyrrhiza extract and discovery of potential markers by fingerprint-activity relationship modeling.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 4;9(1):1309. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38601-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30718789 Free PMC article.
-
Application of fingerprint combined with quantitative analysis and multivariate chemometric methods in quality evaluation of dandelion (Taraxacum mongolicum).R Soc Open Sci. 2021 Oct 27;8(10):210614. doi: 10.1098/rsos.210614. eCollection 2021 Oct. R Soc Open Sci. 2021. PMID: 34729206 Free PMC article.
-
Application of HPLC Fingerprint Combined with Chemical Pattern Recognition and Multi-Component Determination in Quality Evaluation of Echinacea purpurea (L.) Moench.Molecules. 2022 Sep 30;27(19):6463. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196463. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235000 Free PMC article.
-
Quality Evaluation of Mahonia bealei (Fort.) Carr. Using Supercritical Fluid Chromatography with Chemical Pattern Recognition.Molecules. 2019 Oct 13;24(20):3684. doi: 10.3390/molecules24203684. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31614942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Committee . Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. China Chemical Industry Press; Beijing, China: 2015.
-
- Xian Y.F., Lin Z.X., Ip S.P., Su Z.R., Chen J.N., Lai X.P. Comparison of the neuroprotective effect of Cortex Phellodendri chinensis and Cortex Phellodendri amurensis against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Phytomedicine. 2013;20:187–193. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2012.09.028. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhu Z.M., Lai X.X., Su M.X. Determinations of active compositions in Cortex Phellodendri Chinensis and Cortex Phellodendri Amurensis from different areas by HPLC. Clin. Med. Eng. 2011;18:106–108. (In Chinese)
-
- Li L.X., Qiao B., Li Y.B., Zhang L.Y., Wang Y.M., Jin J., Zhang X.X. Changes of chemical constituents in Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex before and after charing based on RPLC/Q-TOF-MS technology. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 2012;43:1314–1319. (In Chinese)
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

