The "Frail" Brain Blood Barrier in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Role of Early Disruption of Endothelial Cell-to-Cell Connections
- PMID: 30201915
- PMCID: PMC6164949
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092693
The "Frail" Brain Blood Barrier in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Role of Early Disruption of Endothelial Cell-to-Cell Connections
Abstract
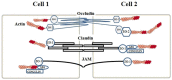
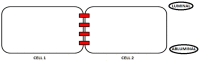
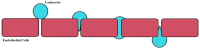
The main neurovascular unit of the Blood Brain Barrier (BBB) consists of a cellular component, which includes endothelial cells, astrocytes, pericytes, microglia, neurons, and oligodendrocytes as well as a non-cellular component resulting from the extracellular matrix. The endothelial cells are the major vital components of the BBB able to preserve the brain homeostasis. These cells are situated along the demarcation line between the bloodstream and the brain. Therefore, an alteration or the progressive disruption of the endothelial layer may clearly impair the brain homeostasis. The proper functioning of the brain endothelial cells is generally ensured by two elements: (1) the presence of junction proteins and (2) the preservation of a specific polarity involving an apical-luminal and a basolateral-abluminal membrane. This review intends to identify the molecular mechanisms underlying BBB function and their changes occurring in early stages of neurodegenerative processes in order to develop novel therapeutic strategies aimed to counteract neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: brain blood barrier; endothelial dysfunction; neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maintaining blood-brain barrier integrity: pericytes perform better than astrocytes during prolonged oxygen deprivation.J Cell Physiol. 2009 Mar;218(3):612-22. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21638. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19016245
-
The abluminal endothelial membrane in neurovascular remodeling in health and disease.Sci Signal. 2012 Aug 7;5(236):re4. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002886. Sci Signal. 2012. PMID: 22871611 Review.
-
A new blood-brain barrier model using primary rat brain endothelial cells, pericytes and astrocytes.Neurochem Int. 2009 Mar-Apr;54(3-4):253-63. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2008.12.002. Epub 2008 Dec 7. Neurochem Int. 2009. PMID: 19111869
-
Blood-brain barrier: structural components and function under physiologic and pathologic conditions.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2006 Sep;1(3):223-36. doi: 10.1007/s11481-006-9025-3. Epub 2006 Jul 6. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 18040800 Review.
-
Morphology and properties of pericytes.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;686:49-68. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-938-3_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21082366 Review.
Cited by
-
The Contribution of Gut Microbiota and Endothelial Dysfunction in the Development of Arterial Hypertension in Animal Models and in Humans.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 28;23(7):3698. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073698. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple-Hit Hypothesis in Parkinson's Disease: LRRK2 and Inflammation.Front Neurosci. 2020 Apr 28;14:376. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00376. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32410948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico study of thymohydroquinone interaction with blood-brain barrier disrupting proteins.Future Sci OA. 2020 Sep 25;6(10):FSO632. doi: 10.2144/fsoa-2020-0115. Future Sci OA. 2020. PMID: 33312701 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption and Its Involvement in Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 3;23(23):15271. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315271. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myelin Disturbances Produced by Sub-Toxic Concentration of Heavy Metals: The Role of Oligodendrocyte Dysfunction.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 14;20(18):4554. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184554. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31540019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Begley D.J., Brightman M.W. Structural and functional aspects of the blood-brain barrier. Prog. Drug. 2003;61:39–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

