Control of Biofilm Formation in Healthcare: Recent Advances Exploiting Quorum-Sensing Interference Strategies and Multidrug Efflux Pump Inhibitors
- PMID: 30201944
- PMCID: PMC6163278
- DOI: 10.3390/ma11091676
Control of Biofilm Formation in Healthcare: Recent Advances Exploiting Quorum-Sensing Interference Strategies and Multidrug Efflux Pump Inhibitors
Abstract
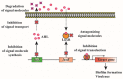
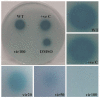
Biofilm formation in healthcare is an issue of considerable concern, as it results in increased morbidity and mortality, imposing a significant financial burden on the healthcare system. Biofilms are highly resistant to conventional antimicrobial therapies and lead to persistent infections. Hence, there is a high demand for novel strategies other than conventional antibiotic therapies to control biofilm-based infections. There are two approaches which have been employed so far to control biofilm formation in healthcare settings: one is the development of biofilm inhibitors based on the understanding of the molecular mechanism of biofilm formation, and the other is to modify the biomaterials which are used in medical devices to prevent biofilm formation. This review will focus on the recent advances in anti-biofilm approaches by interrupting the quorum-sensing cellular communication system and the multidrug efflux pumps which play an important role in biofilm formation. Research efforts directed towards these promising strategies could eventually lead to the development of better anti-biofilm therapies than the conventional treatments.
Keywords: biofilm formation; biofilm inhibition; healthcare; multidrug efflux pumps; quorum sensing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Focused review on dual inhibition of quorum sensing and efflux pumps: A potential way to combat multi drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Nov 1;190:33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.199. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34480904 Review.
-
Role of bacterial efflux pumps in biofilm formation.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018 Aug 1;73(8):2003-2020. doi: 10.1093/jac/dky042. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29506149 Review.
-
Baicalin Inhibits Biofilm Formation and the Quorum-Sensing System by Regulating the MsrA Drug Efflux Pump in Staphylococcus saprophyticus.Front Microbiol. 2019 Dec 10;10:2800. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02800. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31921008 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticles as Efflux Pump and Biofilm Inhibitor to Rejuvenate Bactericidal Effect of Conventional Antibiotics.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2017 Dec;12(1):454. doi: 10.1186/s11671-017-2222-6. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2017. PMID: 28709374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efflux pumps as potential targets for biofilm inhibition.Front Microbiol. 2024 Feb 23;15:1315238. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1315238. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38596384 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quorum Sensing Inhibitors: An Alternative Strategy to Win the Battle against Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Bacteria.Molecules. 2024 Jul 24;29(15):3466. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153466. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39124871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biofilms: Formation, Research Models, Potential Targets, and Methods for Prevention and Treatment.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Oct;9(29):e2203291. doi: 10.1002/advs.202203291. Epub 2022 Aug 28. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 36031384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A global bibliometric and visualized analysis of bacterial biofilm eradication from 2012 to 2022.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 22;14:1287964. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1287964. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38075865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial resistance expansion in pathogens: a review of current mitigation strategies and advances towards innovative therapy.JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2023 Dec 11;5(6):dlad127. doi: 10.1093/jacamr/dlad127. eCollection 2023 Dec. JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2023. PMID: 38089461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibiofilm Strategies in Neonatal and Pediatric Infections.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 May 30;13(6):509. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13060509. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927176 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

