Ectopic expression of aPKC-mediated phosphorylation in p300 modulates hippocampal neurogenesis, CREB binding and fear memory differently with age
- PMID: 30201979
- PMCID: PMC6131509
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-31657-2
Ectopic expression of aPKC-mediated phosphorylation in p300 modulates hippocampal neurogenesis, CREB binding and fear memory differently with age
Abstract
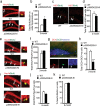
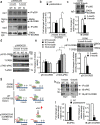
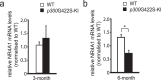
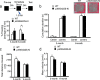
Epigenetic modifications have become an emerging interface that links extrinsic signals to alterations of gene expression that determine cell identity and function. However, direct signaling that regulates epigenetic modifications is unknown. Our previous work demonstrated that phosphorylation of CBP at Ser 436 by atypical protein kinase C (aPKC) regulates age-dependent hippocampal neurogenesis and memory. p300, a close family member of CBP, lacks the aPKC-mediated phosphorylation found in CBP. Here, we use a phosphorylation-competent p300 (G442S) knock-in (KI) mouse model that ectopically expresses p300 phosphorylation in a homologous site to CBP Ser436, and assess its roles in modulating hippocampal neurogenesis, CREB binding ability, and fear memory. Young adult (3 months) p300G422S-KI mice exhibit enhanced hippocampal neurogenesis due to increased cell survival of newly-generated neurons, without alterations in CREB binding and contextual fear memory. On the other hand, mature adult (6 months) p300G422S-KI mice display reduced CREB binding, associated with impaired contextual fear memory without alterations in hippocampal neurogenesis. Additionally, we show that repulsive interaction between pS133-CREB and pS422-p300G422S may contribute to the reduced CREB binding to p300G422S. Together, these data suggest that a single phosphorylation change in p300 has the capability to modulate hippocampal neurogenesis, CREB binding, and associative fear memory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The aPKC-CBP Pathway Regulates Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in an Age-Dependent Manner.Stem Cell Reports. 2016 Oct 11;7(4):719-734. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.08.007. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Stem Cell Reports. 2016. PMID: 27618724 Free PMC article.
-
Serine 133 phosphorylation is not required for hippocampal CREB-mediated transcription and behavior.Learn Mem. 2015 Jan 15;22(2):109-15. doi: 10.1101/lm.037044.114. Print 2015 Feb. Learn Mem. 2015. PMID: 25593297 Free PMC article.
-
Differential role for CBP and p300 CREB-binding domain in motor skill learning.Behav Neurosci. 2006 Jun;120(3):724-9. doi: 10.1037/0735-7044.120.3.724. Behav Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16768624
-
Modulation of Aversive Memory by Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis.Neurotherapeutics. 2017 Jul;14(3):646-661. doi: 10.1007/s13311-017-0528-9. Neurotherapeutics. 2017. PMID: 28488160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CREB and neuronal selection for memory trace.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 Mar 21;7:44. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00044. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 23519079 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prenatal low-dose methylmercury exposure causes premature neuronal differentiation and autism-like behaviors in a rodent model.iScience. 2023 Jan 31;26(3):106093. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106093. eCollection 2023 Mar 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 36843845 Free PMC article.
-
The phosphorylation to acetylation/methylation cascade in transcriptional regulation: how kinases regulate transcriptional activities of DNA/histone-modifying enzymes.Cell Biosci. 2022 Jun 3;12(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00821-7. Cell Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35659740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult Neurogenesis: A Story Ranging from Controversial New Neurogenic Areas and Human Adult Neurogenesis to Molecular Regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 25;22(21):11489. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111489. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768919 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

