Advanced fabrication of biosensor on detection of Glypican-1 using S-Acetylmercaptosuccinic anhydride (SAMSA) modification of antibody
- PMID: 30202003
- PMCID: PMC6131508
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-31994-2
Advanced fabrication of biosensor on detection of Glypican-1 using S-Acetylmercaptosuccinic anhydride (SAMSA) modification of antibody
Abstract
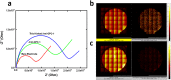
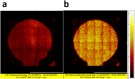
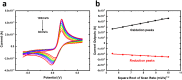
Glypican-1 (GPC-1) has been recognized as biomarker of pancreatic cancer. Quantification of GPC-1 level is also pivotal to breast cancer and prostate cancer's patients. We hereby report the first biosensor for GPC-1 detection. Instead of using crosslinking technique and surface immobilization of antibody, we applied a novel method for biosensor fabrication, using S-Acetylmercaptosuccinic anhydride (SAMSA) to modify the Anti-GPC-1 producing a thiol-linked Anti-GPC-1. The thiol-linked Anti-GPC-1 was then directly formed a single-layer antibody layer on the gold biosensor, minimizing the biosensor preparation steps significantly. Time of Flight Secondary Ions Mass Spectroscopy (TOF-SIMS) characterization verified the thiol-linked antibody layer and demonstrated a unique perspective for surface protein characterization. Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) was applied to quantify GPC-1 antigen in undiluted human serum with a concentration range of 5,000 pg/µL to 100 pg/µL. The performance of this newly designed biosensor was also compared with modified self-assembled monolayer system fabricated biosensor, demonstrating the high-sensitivity and high-reproducibility of the SAMSA modified antibody based biosensor. This simple fabrication method can also expand to detection of other biomolecules. The simplified operation process shows great potential in clinical application development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
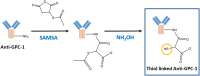
Similar articles
-
Simultaneous voltammetric immunodetection of alpha-fetoprotein and glypican-3 using a glassy carbon electrode modified with magnetite-conjugated dendrimers.Mikrochim Acta. 2019 Mar 23;186(4):255. doi: 10.1007/s00604-019-3354-4. Mikrochim Acta. 2019. PMID: 30904972
-
Application of bioconjugation chemistry on biosensor fabrication for detection of TAR-DNA binding protein 43.Biosens Bioelectron. 2018 Oct 15;117:60-67. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.05.060. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018. PMID: 29885581 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of cancer associated biomarker HER3 based on anti-HER3 biosensor.Talanta. 2014 Mar;120:355-61. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2013.11.090. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Talanta. 2014. PMID: 24468382
-
Antibody orientation on biosensor surfaces: a minireview.Analyst. 2013 Mar 21;138(6):1619-27. doi: 10.1039/c2an36787d. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Analyst. 2013. PMID: 23337971 Review.
-
Clinical development of an anti-GPC-1 antibody for the treatment of cancer.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2022 May;22(5):603-613. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2022.2033204. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35067148 Review.
Cited by
-
A Highly Sensitive Chitosan-Based SERS Sensor for the Trace Detection of a Model Cationic Dye.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 28;25(17):9327. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179327. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273279 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-irradiated synthesis of 3-mercaptopropyl trimethoxysilane-modified hydroxyapatite derived from fish-scale residues followed by ultrasound-assisted organic dyes removal.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 10;11(1):5560. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85206-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33692430 Free PMC article.
-
A high-performance electrochemical aptasensor based on graphene-decorated rhodium nanoparticles to detect HER2-ECD oncomarker in liquid biopsy.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 28;12(1):3299. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07230-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35228597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matsuda K, et al. Glypican-1 is overexpressed in human breast cancer and modulates the mitogenic effects of multiple heparin-binding growth factors in breast cancer cells. Cancer research. 2001;61:5562–5569. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

