Electronic and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Li-Terminated Linear Boron Chains Studied by TAO-DFT
- PMID: 30202018
- PMCID: PMC6131515
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-31947-9
Electronic and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Li-Terminated Linear Boron Chains Studied by TAO-DFT
Abstract
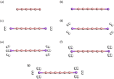
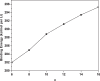
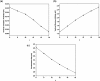
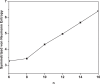
It has been extremely difficult for conventional computational approaches to reliably predict the properties of multi-reference systems (i.e., systems possessing radical character) at the nanoscale. To resolve this, we employ thermally-assisted-occupation density functional theory (TAO-DFT) to predict the electronic and hydrogen storage properties of Li-terminated linear boron chains (Li2Bn), with n boron atoms (n = 6, 8, …, and 16). From our TAO-DFT results, Li2Bn, which possess radical character, can bind up to 4 H2 molecules per Li, with the binding energies in the desirable regime (between 20 and 40 kJ/mol per H2). The hydrogen gravimetric storage capacities of Li2Bn range from 7.9 to 17.0 wt%, achieving the ultimate goal of the United States Department of Energy. Accordingly, Li2Bn could be promising media for storing and releasing H2 at temperatures much higher than the boiling point of liquid nitrogen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

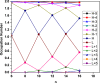
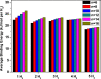


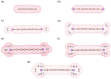
References
-
- Jena P. Materials for hydrogen storage: past, present, and future. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011;2:206–211. doi: 10.1021/jz1015372. - DOI
-
- Durbin D, Malardier-Jugroot C. Review of hydrogen storage techniques for on board vehicle applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2013;38:14595–14617. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.07.058. - DOI
Grants and funding
- MOST104-2628-M-002-011-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan)
- MOST107-2628-M-002-005-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan)
- NTU-CCP-106R891706/National Taiwan University (NTU)
- NTU-CDP-105R7818/National Taiwan University (NTU)
- NTU-CC-107L892906/National Taiwan University (NTU)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

