ABC transporter mis-splicing associated with resistance to Bt toxin Cry2Ab in laboratory- and field-selected pink bollworm
- PMID: 30202031
- PMCID: PMC6131251
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-31840-5
ABC transporter mis-splicing associated with resistance to Bt toxin Cry2Ab in laboratory- and field-selected pink bollworm
Abstract
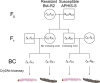
Evolution of pest resistance threatens the benefits of genetically engineered crops that produce Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) insecticidal proteins. Strategies intended to delay pest resistance are most effective when implemented proactively. Accordingly, researchers have selected for and analyzed resistance to Bt toxins in many laboratory strains of pests before resistance evolves in the field, but the utility of this approach depends on the largely untested assumption that laboratory- and field-selected resistance to Bt toxins are similar. Here we compared the genetic basis of resistance to Bt toxin Cry2Ab, which is widely deployed in transgenic crops, between laboratory- and field-selected populations of the pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella), a global pest of cotton. We discovered that resistance to Cry2Ab is associated with mutations disrupting the same ATP-binding cassette transporter gene (PgABCA2) in a laboratory-selected strain from Arizona, USA, and in field-selected populations from India. The most common mutation, loss of exon 6 caused by alternative splicing, occurred in resistant larvae from both locations. Together with previous data, the results imply that mutations in the same gene confer Bt resistance in laboratory- and field-selected strains and suggest that focusing on ABCA2 genes may help to accelerate progress in monitoring and managing resistance to Cry2Ab.
Conflict of interest statement
This is a cooperative investigation between the USDA Agricultural Research Service, the University of Arizona, the Indian Council of Agricultural Research, the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization, and the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology. DuPont Pioneer provided partial support to J.A.F., B.E.T., and Y.C. for this work. J.A.F. is coauthor of a patent “Cadherin Receptor Peptide for Potentiating Bt Biopesticides” (patent numbers: US20090175974A1, US8354371, WO2009067487A2, WO2009067487A3). B.E.T. is a coauthor of a patent on modified Bt toxins, “Suppression of Resistance in Insects to
Figures


Similar articles
-
Shared and Independent Genetic Basis of Resistance to Bt Toxin Cry2Ab in Two Strains of Pink Bollworm.Sci Rep. 2020 May 14;10(1):7988. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64811-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32409635 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-mediated mutations in the ABC transporter gene ABCA2 confer pink bollworm resistance to Bt toxin Cry2Ab.Sci Rep. 2021 May 17;11(1):10377. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89771-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34001946 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Toxin Resistance Enables Pink Bollworm Survival on Pyramided Bt Cotton.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 12;5:16554. doi: 10.1038/srep16554. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26559899 Free PMC article.
-
Early detection of field-evolved resistance to Bt cotton in China: cotton bollworm and pink bollworm.J Invertebr Pathol. 2012 Jul;110(3):301-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2012.04.008. Epub 2012 Apr 16. J Invertebr Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22537835 Review.
-
Sustained susceptibility of pink bollworm to Bt cotton in the United States.GM Crops Food. 2012 Jul-Sep;3(3):194-200. doi: 10.4161/gmcr.20329. Epub 2012 Jul 1. GM Crops Food. 2012. PMID: 22572905 Review.
Cited by
-
Insect ATP-Binding Cassette (ABC) Transporters: Roles in Xenobiotic Detoxification and Bt Insecticidal Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 10;20(11):2829. doi: 10.3390/ijms20112829. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31185645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors Related to Bacillus thuringiensis and Gut Physiology. Comment on Rajan, V. An Alkaline Foregut Protects Herbivores from Latex in Forage, but Increases Their Susceptibility to Bt Endotoxin. Life 2023, 13, 2195.Life (Basel). 2024 Jan 31;14(2):205. doi: 10.3390/life14020205. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38398714 Free PMC article.
-
Shared and Independent Genetic Basis of Resistance to Bt Toxin Cry2Ab in Two Strains of Pink Bollworm.Sci Rep. 2020 May 14;10(1):7988. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64811-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32409635 Free PMC article.
-
A Hierarchical Error Correction Strategy for Text DNA Storage.Interdiscip Sci. 2022 Mar;14(1):141-150. doi: 10.1007/s12539-021-00476-x. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Interdiscip Sci. 2022. PMID: 34463928
-
The Spodoptera exigua ABCC2 Acts as a Cry1A Receptor Independently of its Nucleotide Binding Domain II.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Mar 22;11(3):172. doi: 10.3390/toxins11030172. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30909393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Genetically Engineered Crops: Experiences and Prospects (National Academies Press, Washington, DC, 2016). - PubMed
-
- ISAAA. Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops in 2017: Biotech crop adoption surges as economic benefits accumulate in 22 years. ISAAA Brief No. 53 (ISAAA, Ithaca, NY).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

