De novo assembly, characterization, functional annotation and expression patterns of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) transcriptome
- PMID: 30202061
- PMCID: PMC6131155
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-31148-4
De novo assembly, characterization, functional annotation and expression patterns of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) transcriptome
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: De novo assembly, characterization, functional annotation and expression patterns of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) transcriptome.Sci Rep. 2022 May 4;12(1):7277. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11096-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35508513 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
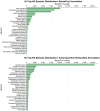
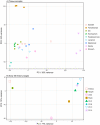
The black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) remains the second most widely cultured shrimp species globally; however, issues with disease and domestication have seen production levels stagnate over the past two decades. To help identify innovative solutions needed to resolve bottlenecks hampering the culture of this species, it is important to generate genetic and genomic resources. Towards this aim, we have produced the most complete publicly available P. monodon transcriptome database to date based on nine adult tissues and eight early life-history stages (BUSCO - Complete: 98.2% [Duplicated: 51.3%], Fragmented: 0.8%, Missing: 1.0%). The assembly resulted in 236,388 contigs, which were then further segregated into 99,203 adult tissue specific and 58,678 early life-history stage specific clusters. While annotation rates were low (approximately 30%), as is typical for a non-model organisms, annotated transcript clusters were successfully mapped to several hundred functional KEGG pathways. Transcripts were clustered into groups within tissues and early life-history stages, providing initial evidence for their roles in specific tissue functions, or developmental transitions. We expect the transcriptome to provide an essential resource to investigate the molecular basis of commercially relevant-significant traits in P. monodon and other shrimp species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- FAO. Fisheries and Aquaculture topics. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture (SOFIA) (Food and Agriculture Organization United Nations, 2016).
-
- Gjedrem T, Robinson N, Rye M. The importance of selective breeding in aquaculture to meet future demands for animal protein: a review. Aquaculture. 2012;350:117–129. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.04.008. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

