A PECTIN METHYLESTERASE gene at the maize Ga1 locus confers male function in unilateral cross-incompatibility
- PMID: 30202064
- PMCID: PMC6131150
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06139-8
A PECTIN METHYLESTERASE gene at the maize Ga1 locus confers male function in unilateral cross-incompatibility
Abstract
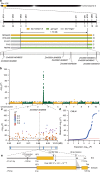
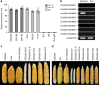
Unilateral cross-incompatibility (UCI) is a unidirectional inter/intra-population reproductive barrier when both parents are self-compatible. Maize Gametophyte factor1 (Ga1) is an intraspecific UCI system and has been utilized in breeding. However, the mechanism underlying maize UCI specificity has remained mysterious for decades. Here, we report the cloning of ZmGa1P, a pollen-expressed PECTIN METHYLESTERASE (PME) gene at the Ga1 locus that can confer the male function in the maize UCI system. Homozygous transgenic plants expressing ZmGa1P in a ga1 background can fertilize Ga1-S plants and can be fertilized by pollen of ga1 plants. ZmGa1P protein is predominantly localized to the apex of growing pollen tubes and may interact with another pollen-specific PME protein, ZmPME10-1, to maintain the state of pectin methylesterification required for pollen tube growth in Ga1-S silks. Our study discloses a PME-mediated UCI mechanism and provides a tool to manipulate hybrid breeding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- United States Department of Agriculture Foreign Agricultural Service. https://www.fas.usda.gov/data/grain-world-markets-and-trade 2016.
-
- Nelson, O. E. in The Maize Handbook, M. Freeling, V. Walbot, Eds. (Springer New York, 1994), 496–503.
-
- Liu X, et al. Fine mapping of the maize cross-incompatibility locus using a homogeneous population. Crop Sci. 2014;54:873–881. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2013.09.0598. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2016ZX08010-002/Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China (Ministry of Agriculture)/International
- 91535105 and 31271729/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)/International
- 2016094 and 2017136/Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Youth Innovation Promotion Association, CAS)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

