Laser guided ionic wind
- PMID: 30202066
- PMCID: PMC6131152
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-31993-3
Laser guided ionic wind
Abstract
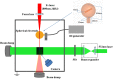
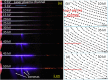
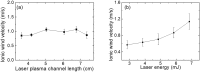
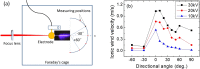
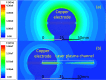
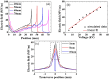
We report on a method to experimentally generate ionic wind by coupling an external large electric field with an intense femtosecond laser induced air plasma channel. The measured ionic wind velocity could be as strong as >4 m/s. It could be optimized by increasing the strength of the applied electric field and the volume of the laser induced plasma channel. The experimental observation was qualitatively confirmed by a numerical simulation of spatial distribution of the electric field. The ionic wind can be generated outside a high-voltage geometry, even at remote distances.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Robinson M. A history of the electric wind. American Journal of Physics. 1962;30:366–372. doi: 10.1119/1.1942021. - DOI
-
- Goldman M, Goldman A, Sigmond RS. The corona discharge, its properties and specific uses. Pure & Applied Chemistry. 1985;57:1353–1362. doi: 10.1351/pac198557091353. - DOI
-
- Moreau E. Airflow control by non-thermal plasma actuators. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics. 2007;40:605–636. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/40/3/S01. - DOI
-
- Rayman MD, Lehman DH. Deep Space One: NASA’s first deep-space technology validation mission. Acta Astronautica. 1997;41:289–299. doi: 10.1016/S0094-5765(98)00073-3. - DOI
-
- Rayman MD. The Deep Space 1 extended mission: challenges in preparing for an encounter with comet Borrelly. Acta Astronautica. 2002;51:507–516. doi: 10.1016/S0094-5765(02)00070-X. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

