Downregulation of hypermethylated in cancer-1 by miR- 4532 promotes adriamycin resistance in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 30202238
- PMCID: PMC6123967
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-018-0616-x
Downregulation of hypermethylated in cancer-1 by miR- 4532 promotes adriamycin resistance in breast cancer cells
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs are small RNAs (~ 22 nt) that modulate the expression of thousands of genes in tumors and play important roles in the formation of multidrug resistance. In this study, we firstly investigated that miR-4532 involved in the multidrug resistance formation of breast cancer by targeting hypermethylated in cancer 1 (HIC-1), a tumor-suppressor gene.
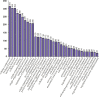
Methods: To identify and characterize the possible miRNAs in regulating multidrug resistance, we employed the transcriptome sequencing approach to profile the changes in the expression of miRNAs and their target mRNAs were obtained by bioinformatics prediction. Then the molecular biology experiments were conducted to confirm miR-4532 involved in multidrug resistance formation of breast cancer.
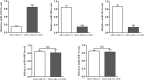
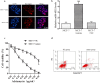
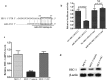
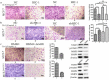
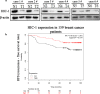
Results: The luciferase reporter assay experiment was employed to confirm that HIC-1 was the target of miR-4532. Transfection with an miR-4532 mimic indicated miR-4532 mimic significantly increased breast cancer cell resistance to adriamycin. Cell proliferation and invasion assay experiments showed overexpression of HIC-1 inhibited the invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells. Meanwhile, the interleukin (IL)-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway was confirmed to be involving in multidrug resistance by western blotting experiments.
Conclusions: These results suggest that downregulation of hypermethylated in cancer-1 by miR-4532 could promote adriamycin resistance in breast cancer cells, in which the IL-6/STAT3 pathway was regulated by the HIC-1. This finding might contribute to new therapeutic target for reversal of tumor resistance.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Hypermethylated in cancer-1; Interleukin-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathway; Multidrug resistance; miR-4532.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Downregulation of the tumor-suppressor miR-16 via progestin-mediated oncogenic signaling contributes to breast cancer development.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 May 14;14(3):R77. doi: 10.1186/bcr3187. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22583478 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-124 enhances response to radiotherapy in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer cells by targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.Croat Med J. 2016 Oct 31;57(5):457-464. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2016.57.457. Croat Med J. 2016. PMID: 27815936 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-29a contributes to drug-resistance of breast cancer cells to adriamycin through PTEN/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway.Gene. 2016 Nov 15;593(1):84-90. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.08.016. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Gene. 2016. PMID: 27523474
-
miR-519d-mediated downregulation of STAT3 suppresses breast cancer progression.Oncol Rep. 2015 Oct;34(4):2188-94. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4160. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26238950
-
STAT3 is involved in miR-124-mediated suppressive effects on esophageal cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2015 Apr 19;15:306. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1303-0. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25928665 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive serum and tissue microRNA profiling in dedifferentiated liposarcoma.Oncol Lett. 2021 Aug;22(2):623. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12884. Epub 2021 Jun 29. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34285721 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of urinary exosomal microRNA biomarkers for the diagnosis of acute rejection in kidney transplant recipients.Front Immunol. 2023 May 9;14:1190576. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1190576. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37228607 Free PMC article.
-
Acute myeloid leukemia cells secrete microRNA-4532-containing exosomes to mediate normal hematopoiesis in hematopoietic stem cells by activating the LDOC1-dependent STAT3 signaling pathway.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Dec 16;10(1):384. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1475-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31842997 Free PMC article.
-
HNRNPA2/B1 is upregulated in endocrine-resistant LCC9 breast cancer cells and alters the miRNA transcriptome when overexpressed in MCF-7 cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 1;9(1):9430. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45636-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31263129 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of Potential miRNA Biomarkers and Prediction for Ovarian Cancer Using Artificial Intelligence.Front Genet. 2021 Nov 25;12:724785. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.724785. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34899827 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

