Overexpression of the Drosophila ATR homologous checkpoint kinase Mei-41 induces a G2/M checkpoint in Drosophila imaginal tissue
- PMID: 30202398
- PMCID: PMC6125995
- DOI: 10.1186/s41065-018-0066-4
Overexpression of the Drosophila ATR homologous checkpoint kinase Mei-41 induces a G2/M checkpoint in Drosophila imaginal tissue
Abstract
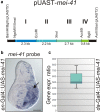
Background: DNA damage generally results in the activation of ATM/ATR kinases and the downstream checkpoint kinases Chk1/Chk2. In Drosophila melanogaster, the ATR homologue meiotic 41 (mei-41) is pivotal to DNA damage repair and cell cycle checkpoint signalling. Although various mei-41 mutant alleles have been analyzed in the past, no gain-of-function allele is yet available. To fill this gap, we have generated transgenic flies allowing temporal and tissue-specific induction of mei-41.
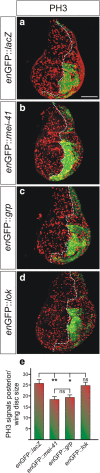
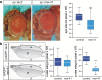
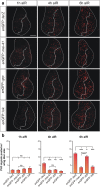
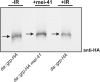
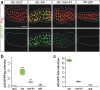
Results: Overexpression of mei-41 in wing and eye anlagen affects proliferation and a G2/M checkpoint even in the absence of genomic stress. Similar consequences were observed following the overexpression of the downstream kinase Grapes (Grp) but not of Loki (Lok), encoding the respective Drosophila Chk1 and Chk2 homologues, in agreement with their previously reported activities. Moreover, we show that irradiation induced cell cycle arrest was prolonged in the presence of ectopic mei-41 expression. Similar to irradiation stress, mei-41 triggered the occurrence of a slower migrating form of Grp, implying specific phosphorylation of Grp in response to either signal. Using a p53R-GFP biosensor, we further show that overexpression of mei-41 was sufficient to elicit a robust p53 activation in vivo.
Conclusion: We conclude that overexpression of the Drosophila ATR homologue mei-41 elicits an effectual DNA damage response irrespective of irradiation.
Keywords: ATR; DNA damage checkpoint; Mei-41; Overexpression; p53 activation.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.Not applicable.The authors declare that there are no competing financial, personal, or professional interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Grp/DChk1 is required for G2-M checkpoint activation in Drosophila S2 cells, whereas Dmnk/DChk2 is dispensable.J Cell Sci. 2005 May 1;118(Pt 9):1833-42. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02309. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 15860729 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila Claspin is required for the G2 arrest that is induced by DNA replication stress but not by DNA double-strand breaks.DNA Repair (Amst). 2012 Sep 1;11(9):741-52. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2012.06.007. Epub 2012 Jul 15. DNA Repair (Amst). 2012. PMID: 22796626
-
Drosophila ATR in double-strand break repair.Genetics. 2007 Mar;175(3):1023-33. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.067330. Epub 2006 Dec 28. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17194776 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage checkpoint kinases in cancer.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2020 Jun 8;22:e2. doi: 10.1017/erm.2020.3. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32508294 Review.
-
The multiple checkpoint functions of CHK1 and CHK2 in maintenance of genome stability.Front Biosci. 2008 May 1;13:5016-29. doi: 10.2741/3060. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 18508566 Review.
Cited by
-
Duox-generated reactive oxygen species activate ATR/Chk1 to induce G2 arrest in Drosophila tracheoblasts.Elife. 2021 Oct 8;10:e68636. doi: 10.7554/eLife.68636. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34622778 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Wnts act synergistically to induce Chk1/Grapes expression and mediate G2 arrest in Drosophila tracheoblasts.Elife. 2020 Sep 2;9:e57056. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57056. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32876044 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic instability and cancer: lessons from Drosophila.Open Biol. 2020 Jun;10(6):200060. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200060. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Open Biol. 2020. PMID: 32485126 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Song YH. Drosophila melanogaster: a model for the study of DNA damage checkpoint response. Mol Cells. 2005;19:167–179. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

