Hydroarylations by cobalt-catalyzed C-H activation
- PMID: 30202481
- PMCID: PMC6122362
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.14.202
Hydroarylations by cobalt-catalyzed C-H activation
Abstract
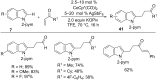
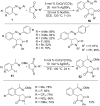
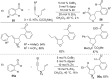
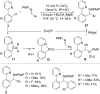
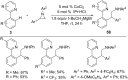
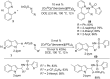
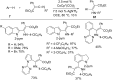
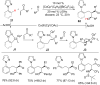
As an earth-abundant first-row transition metal, cobalt catalysts offer a broad range of economical methods for organic transformations via C-H activation. One of the transformations is the addition of C-H to C-X multiple bonds to afford alkylation, alkenation, amidation, and cyclization products using low- or high-valent cobalt catalysts. This hydroarylation is an efficient approach to build new C-C bonds in a 100% atom-economical manner. In this review, the recent developments of Co-catalyzed hydroarylation reactions and their mechanistic studies are summarized.
Keywords: C–H activation; C−C formation; catalysis; cobalt; hydroarylation.
Figures




















Similar articles
-
Low-valent cobalt catalysis: new opportunities for C-H functionalization.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Apr 15;47(4):1208-19. doi: 10.1021/ar400270x. Epub 2014 Feb 27. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 24576170
-
Cobalt catalysis involving π components in organic synthesis.Acc Chem Res. 2015 Apr 21;48(4):1194-206. doi: 10.1021/ar500463r. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Acc Chem Res. 2015. PMID: 25854540
-
Exploration of earth-abundant transition metals (Fe, Co, and Ni) as catalysts in unreactive chemical bond activations.Acc Chem Res. 2015 Mar 17;48(3):886-96. doi: 10.1021/ar500345f. Epub 2015 Feb 13. Acc Chem Res. 2015. PMID: 25679917
-
Manganese-catalyzed hydroarylation of multiple bonds.Org Biomol Chem. 2023 Jan 18;21(3):441-464. doi: 10.1039/d2ob01674e. Org Biomol Chem. 2023. PMID: 36541044 Review.
-
Ruthenium-catalyzed hydroarylation reactions as the strategy towards the synthesis of alkylated arenes and substituted alkenes.RSC Adv. 2023 Feb 21;13(9):6246-6263. doi: 10.1039/d3ra00211j. eCollection 2023 Feb 14. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 36825293 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of Homoallylic Alcohols with Acyclic Quaternary Centers through CoIII -Catalyzed Three-Component C-H Bond Addition to Internally Substituted Dienes and Carbonyls.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Sep 2;58(36):12590-12594. doi: 10.1002/anie.201906633. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 31310435 Free PMC article.
-
C-H Activation by Isolable Cationic Bis(phosphine) Cobalt(III) Metallacycles.J Am Chem Soc. 2022 Oct 19;144(41):19186-19195. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c08865. Epub 2022 Oct 4. J Am Chem Soc. 2022. PMID: 36194198 Free PMC article.
-
Cp*Co(III)-Catalyzed C-H Hydroarylation of Alkynes and Alkenes and Beyond: A Versatile Synthetic Tool.ACS Omega. 2020 Sep 15;5(39):24974-24993. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03639. eCollection 2020 Oct 6. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33043175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three-Component Coupling of Arenes, Ethylene, and Alkynes Catalyzed by a Cationic Bis(phosphine) Cobalt Complex: Intercepting Metallacyclopentenes for C-H Functionalization.J Am Chem Soc. 2022 Mar 16;144(10):4530-4540. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c12646. Epub 2022 Mar 4. J Am Chem Soc. 2022. PMID: 35245039 Free PMC article.
-
Ni-catalyzed hydroarylation of alkynes with unactivated β-C(sp2)-H bonds.Nat Commun. 2022 May 26;13(1):2938. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30367-8. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35618702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cathcart C. Chem Ind. 1990;5:684–687.
-
- Anastas P T, Williamson T C. Green Chemistry. Vol. 626. Washington, DC, U.S.A.: American Chemical Society; 1996. Green Chemistry: An Overview; pp. 1–17. ((ACS Symposium Series)). - DOI
-
- Trost B M. Angew Chem, Int Ed Engl. 1995;34:259–281. doi: 10.1002/anie.199502591. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
