The enzymes of microbial nicotine metabolism
- PMID: 30202483
- PMCID: PMC6122326
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.14.204
The enzymes of microbial nicotine metabolism
Abstract
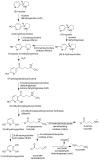
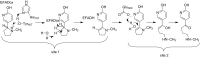
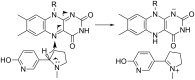
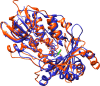
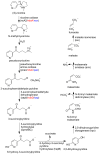
Because of nicotine's toxicity and the high levels found in tobacco and in the waste from tobacco processing, there is a great deal of interest in identifying bacteria capable of degrading it. A number of microbial pathways have been identified for nicotine degradation. The first and best-understood is the pyridine pathway, best characterized for Arthrobacter nicotinovorans, in which the first reaction is hydroxylation of the pyridine ring. The pyrrolidine pathway, which begins with oxidation of a carbon-nitrogen bond in the pyrrolidine ring, was subsequently characterized in a number of pseudomonads. Most recently, a hybrid pathway has been described, which incorporates the early steps in the pyridine pathway and ends with steps in the pyrrolidine pathway. This review summarizes the present status of our understanding of these pathways, focusing on what is known about the individual enzymes involved.
Keywords: biodegradation; enzyme mechanism; flavoprotein; metabolic pathway; nicotine.
Figures
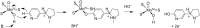




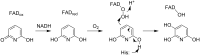

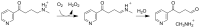


References
-
- Brandsch R, Hinkkanen A E, Decker K. Arch Microbiol. 1982;132:26–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00690812. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
