High-Mobility Group Box-1 and Liver Disease
- PMID: 30202816
- PMCID: PMC6128227
- DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1223
High-Mobility Group Box-1 and Liver Disease
Abstract
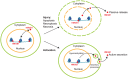
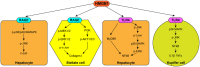
High-mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) is a ubiquitous protein. While initially thought to be simply an architectural protein due to its DNA-binding ability, evidence from the last decade suggests that HMGB1 is a key protein participating in the pathogenesis of acute liver injury and chronic liver disease. When it is passively released or actively secreted after injury, HMGB1 acts as a damage-associated molecular pattern that communicates injury and inflammation to neighboring cells by the receptor for advanced glycation end products or toll-like receptor 4, among others. In the setting of acute liver injury, HMGB1 participates in ischemia/reperfusion, sepsis, and drug-induced liver injury. In the context of chronic liver disease, it has been implicated in alcoholic liver disease, liver fibrosis, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Recently, specific posttranslational modifications have been identified that could condition the effects of the protein in the liver. Here, we provide a detailed review of how HMGB1 signaling participates in acute liver injury and chronic liver disease.
Figures

References
-
- Johns E. The Chromosomal Proteins. Elsevier Science; 2012.
-
- Bustin M, Reeves R. High‐mobility‐group chromosomal proteins: architectural components that facilitate chromatin function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 1996;54:35‐100. - PubMed
-
- Bustin M, Lehn DA, Landsman D. Structural features of the HMG chromosomal proteins and their genes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1990;1049:231‐243. - PubMed
-
- Stros M. HMGB proteins: interactions with DNA and chromatin. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010;1799:101‐113. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

