Chemical Activation of the Constitutive Androstane Receptor Leads to Activation of Oxidant-Induced Nrf2
- PMID: 30203046
- PMCID: PMC6317430
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfy231
Chemical Activation of the Constitutive Androstane Receptor Leads to Activation of Oxidant-Induced Nrf2
Abstract
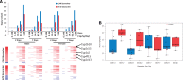
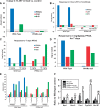
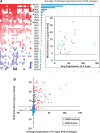
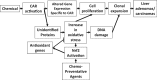
Exposure to environmentally relevant chemicals that activate the xenobiotic receptors aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) in rodent test systems often leads to increases in oxidative stress (OS) that contributes to liver cancer induction. We hypothesized that activation of the oxidant-induced transcription factor Nrf2 could be used as a surrogate endpoint for increases in OS. We examined the relationships between activation of xenobiotic receptors and Nrf2 using previously characterized gene expression biomarkers that accurately predict modulation. Using a correlation approach (Running Fisher Test), the biomarkers were compared with microarray profiles in a mouse liver gene expression compendium. Out of the 163 chemicals examined, 47% from 53 studies activated Nrf2. We found consistent coupling between CAR and Nrf2 activation. Out of the 41 chemicals from 32 studies that activated CAR, 90% also activated Nrf2. CAR was activated earlier and at lower doses than Nrf2, indicating CAR activation preceded Nrf2 activation. Nrf2 activation by 2 CAR activators was abolished in CAR-null mice. We hypothesized that Nrf2 is activated by reactive oxygen species from the increased activity of enzymes encoded by Cyp2b family members. However, Nrf2 was similarly activated in the livers of both TCPOBOP-treated wild-type and Cyp2b9/10/13-null mice. This study provides evidence that Nrf2 activation (1) often occurs after exposure to xenobiotic chemicals, (2) is tightly linked to activation of CAR, and (3) does not require induction of 3 Cyp2b genes secondary to CAR activation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Drug metabolizing enzyme induction pathways in experimental non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.Arch Toxicol. 2008 Dec;82(12):959-64. doi: 10.1007/s00204-008-0312-z. Epub 2008 May 17. Arch Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18488193 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) mediates dieldrin-induced liver tumorigenesis in mouse.Arch Toxicol. 2020 Aug;94(8):2873-2884. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02781-8. Epub 2020 May 20. Arch Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32435917
-
Compensatory changes in CYP expression in three different toxicology mouse models: CAR-null, Cyp3a-null, and Cyp2b9/10/13-null mice.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 28;12(3):e0174355. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174355. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28350814 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of phase I, II and III drug metabolism/transport by xenobiotics.Arch Pharm Res. 2005 Mar;28(3):249-68. doi: 10.1007/BF02977789. Arch Pharm Res. 2005. PMID: 15832810 Review.
-
Cytochrome P450 Induction and Xeno-Sensing Receptors Pregnane X Receptor, Constitutive Androstane Receptor, Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α at the Crossroads of Toxicokinetics and Toxicodynamics.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 Sep;123 Suppl 5:42-50. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13004. Epub 2018 Apr 29. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29527807 Review.
Cited by
-
Associations of persistent organic pollutants in human adipose tissue with retinoid levels and their relevance to the redox microenvironment.Environ Res. 2021 Apr;195:110764. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.110764. Epub 2021 Jan 23. Environ Res. 2021. PMID: 33497679 Free PMC article.
-
Application of a Rat Liver Drug Bioactivation Transcriptional Response Assay Early in Drug Development That Informs Chemically Reactive Metabolite Formation and Potential for Drug-induced Liver Injury.Toxicol Sci. 2020 Sep 1;177(1):281-299. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfaa088. Toxicol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32559301 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic Transcriptome Comparative In Silico Analysis Reveals Similar Pathways and Targets Altered by Legacy and Alternative Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Mice.Toxics. 2023 Nov 28;11(12):963. doi: 10.3390/toxics11120963. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 38133364 Free PMC article.
-
A Collaborative Initiative to Establish Genomic Biomarkers for Assessing Tumorigenic Potential to Reduce Reliance on Conventional Rodent Carcinogenicity Studies.Toxicol Sci. 2022 Jun 28;188(1):4-16. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfac041. Toxicol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35404422 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug Resistance-Associated Protein 2 Deficiency Aggravates Estrogen-Induced Impairment of Bile Acid Metabolomics in Rats.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 21;13:859294. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.859294. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35388287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed S. S., Napoli K. L., Strobel H. W. (1995). Oxygen radical formation during cytochrome P450-catalyzed cyclosporine metabolism in rat and human liver microsomes at varying hydrogen ion concentrations. Mol. Cell Biochem. 151, 131–140. - PubMed
-
- Becuwe P., Dauça M. (2005). Comparison of cytotoxicity induced by hypolipidemic drugs via reactive oxygen species in human and rodent liver cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 16, 483–492. - PubMed
-
- Bondy S. C., Naderi S. (1994). Contribution of hepatic cytochrome P450 systems to the generation of reactive oxygen species. Biochem. Pharmacol. 48, 155–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

