Heparin-binding protein in ventilator-induced lung injury
- PMID: 30203380
- PMCID: PMC6131685
- DOI: 10.1186/s40635-018-0198-x
Heparin-binding protein in ventilator-induced lung injury
Abstract
Background: Although mechanical ventilation is often lifesaving, it can also cause injury to the lungs. The lung injury is caused by not only high pressure and mechanical forces but also by inflammatory processes that are not fully understood. Heparin-binding protein (HBP), released by activated granulocytes, has been indicated as a possible mediator of increased vascular permeability in the lung injury associated with trauma and sepsis. We investigated if HBP levels were increased in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) or plasma in a pig model of ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI). We also investigated if HBP was present in BALF from healthy volunteers and in intubated patients in the intensive care unit (ICU).
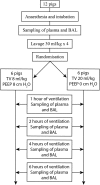
Methods: Anaesthetized pigs were randomized to receive ventilation with either tidal volumes of 8 ml/kg (controls, n = 6) or 20 ml/kg (VILI group, n = 6). Plasma and BALF samples were taken at 0, 1, 2, 4, and 6 h. In humans, HBP levels in BALF were sampled from 16 healthy volunteers and from 10 intubated patients being cared for in the ICU.
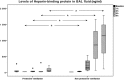
Results: Plasma levels of HBP did not differ between pigs in the control and VILI groups. The median HBP levels in BALF were higher in the VILI group after 6 h of ventilation compared to those in the controls (1144 ng/ml (IQR 359-1636 ng/ml) versus 89 ng/ml (IQR 33-191 ng/ml) ng/ml, respectively, p = 0.02). The median HBP level in BALF from healthy volunteers was 0.90 ng/ml (IQR 0.79-1.01 ng/ml) as compared to 1959 ng/ml (IQR 612-3306 ng/ml) from intubated ICU patients (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: In a model of VILI in pigs, levels of HBP in BALF increased over time compared to controls, while plasma levels did not differ between the two groups. HBP in BALF was high in intubated ICU patients in spite of the seemingly non-harmful ventilation, suggesting that inflammation from other causes might increase HBP levels.
Keywords: HBP; Neutrophils; Pigs; Ventilator-induced lung injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Pigs were used after ethical permission from the Umeå Animal Experimental Ethics Committee (D. nr. A43-12). All procedures were carried out in accordance with the US Public Health Service Policy on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (1996) prepared by the National Academy of Sciences’ Institute for Laboratory Animal Research.
The study on healthy volunteers was approved by the Umeå University Ethics Committee (D.nr. 2018-30-32M(07-099M)). All subjects gave their written informed consent.
For the ICU patients, the regional ethics review board in Linköping gave ethical approval (D.nr. 2010/427-31, 30/9 2011). Oral consent was given by the next of kin.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The company Hansa Medical has filed a patent for HBP as a diagnostic tool in sepsis, and Heiko Herwald is listed as one of the inventors. The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

