Neratinib augments the lethality of [regorafenib + sildenafil]
- PMID: 30203445
- PMCID: PMC6322207
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.27276
Neratinib augments the lethality of [regorafenib + sildenafil]
Abstract
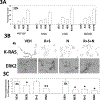
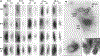
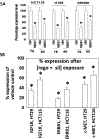
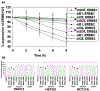
Regorafenib is approved for the treatment of colorectal cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma. In the trial NCT02466802, we have discovered that regorafenib can be safely combined with the phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor sildenafil in advanced solid tumor patients. The present studies determined whether the approved ERBB1/2/4 and RAS downregulating drug neratinib, could enhance the lethality of [regorafenib + sildenafil]. Neratinib enhanced [regorafenib + sildenafil] lethality in a greater than additive fashion in colon cancer cells. The drug combination reduced the expression of mutant K-RAS and of multiple histone deacetylase (HDAC) proteins that required autophagosome formation. It caused green fluorescent protein or red fluorescent protein-tagged forms of K-RAS V12 to localize into large intracellular vesicles. Compared with [regorafenib + sildenafil], the three-drug combination caused greater and more prolonged activation of the ATM-AMPK-ULK-1 pathway and caused a greater suppression and prolonged inactivation of mammalian target of rapamycin, AKT, and p70 S6K. Approximately 70% of enhanced lethality caused by neratinib required ataxia-telangiectasia-mutated (ATM)-AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK) signaling whereas knockdown of Beclin1, ATG5, FADD, and CD95 completely prevented the elevated killing effect. Exposure of cells to [regorafenib + sildenafil] reduced the expression of the checkpoint immunotherapy biomarkers programmed death-ligand 1, ornithine decarboxylase, and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-1 and increased the expression of major histocompatibility complex A (MHCA), which also required autophagosome formation. Knockdown of specific HDAC proteins recapitulated the effects observed using chemical agents. In vivo, using mouse cancer models, neratinib significantly enhanced the antitumor efficacy of [regorafenib + sildenafil]. Our data support performing a new three drug Phase I trial combining regorafenib, sildenafil, and neratinib.
Keywords: DNA damage; HDAC; autophagy.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
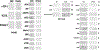
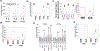
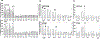




References
-
- Booth L, Shuch B, Albers T, Roberts JL, Tavallai M, Proniuk S, Zukiwski A, Wang D, Chen CS, Bottaro D, Ecroyd H, Lebedyeva IO, Dent P. (2016b) Multi-kinase inhibitors can associate with heat shock proteins through their NH2-termini by which they suppress chaperone function. Oncotarget. 7:12975–96. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

