Establishment of peripheral blood mononuclear cell-derived humanized lung cancer mouse models for studying efficacy of PD-L1/PD-1 targeted immunotherapy
- PMID: 30204048
- PMCID: PMC6284590
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2018.1518948
Establishment of peripheral blood mononuclear cell-derived humanized lung cancer mouse models for studying efficacy of PD-L1/PD-1 targeted immunotherapy
Abstract
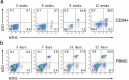
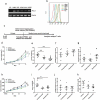
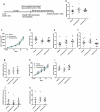
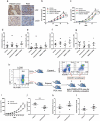
Animal models used to evaluate efficacies of immune checkpoint inhibitors are insufficient or inaccurate. We thus examined two xenograft models used for this purpose, with the aim of optimizing them. One method involves the use of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and cell line-derived xenografts (PBMCs-CDX model). For this model, we implanted human lung cancer cells into NOD-scid-IL2Rg-/- (NSI) mice, followed by injection of human PBMCs. The second method involves the use of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and CDX (HSPCs-CDX model). For this model, we first reconstituted the human immune system by transferring human CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs-derived humanized model) and then transplanted human lung cancer cells. We found that the PBMCs-CDX model was more accurate in evaluating PD-L1/PD-1 targeted immunotherapies. In addition, it took only four weeks with the PBMCs-CDX model for efficacy evaluation, compared to 10-14 weeks with the HSPCs-CDX model. We then further established PBMCs-derived patient-derived xenografts (PDX) models, including an auto-PBMCs-PDX model using cancer and T cells from the same tumor, and applied them to assess the antitumor efficacies of anti-PD-L1 antibodies. We demonstrated that this PBMCs-derived PDX model was an invaluable tool to study the efficacies of PD-L1/PD-1 targeted cancer immunotherapies. Overall, we found our PBMCs-derived models to be excellent preclinical models for studying immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Keywords: Non-small-cell-lung cancer; anti-PD-L1/PD-1 monoclonal antibody; humanized mouse model; immunotherapy; patient-derived-xenograft.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Establishment of humanized tumor microenvironment mouse models based on the injection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and IFN-γ to evaluate the efficacy of PD-L1/PD-1-targeted immunotherapy.Cancer Biol Ther. 2020;21(2):130-138. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2019.1670520. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Cancer Biol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31690181 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of anti-PD-1-based therapy against triple-negative breast cancer patient-derived xenograft tumors engrafted in humanized mouse models.Breast Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 5;20(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s13058-018-1037-4. Breast Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30185216 Free PMC article.
-
Humanized mice in studying efficacy and mechanisms of PD-1-targeted cancer immunotherapy.FASEB J. 2018 Mar;32(3):1537-1549. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700740R. Epub 2018 Jan 3. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29146734 Free PMC article.
-
Role of immune-checkpoint inhibitors in lung cancer.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2018 Jan-Dec;12:1753465817750075. doi: 10.1177/1753465817750075. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2018. PMID: 29385894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2017 Feb;31(1):131-141. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2016.08.004. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2017. PMID: 27912829 Review.
Cited by
-
Autologous humanized mouse models to study combination and single-agent immunotherapy for colorectal cancer patient-derived xenografts.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 21;12:994333. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.994333. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36212401 Free PMC article.
-
Humanized Mouse Models for Immuno-Oncology Research: A Review and Implications in Lung Cancer Research.JTO Clin Res Rep. 2024 Dec 18;6(3):100781. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2024.100781. eCollection 2025 Mar. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2024. PMID: 39990135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PARP inhibitor radiosensitization enhances anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy through stabilizing chemokine mRNA in small cell lung cancer.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 4;16(1):2166. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57257-z. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40038278 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-Based Biomarkers as Predictive and Prognostic Factors in Immunotherapy-Treated Patients with Solid Tumors-Currents and Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 16;17(12):2001. doi: 10.3390/cancers17122001. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p.P476S mutation of RBPJL inhibits the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma by blunting T-cell responses.Clin Transl Immunology. 2020 Sep 16;9(9):e1172. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1172. eCollection 2020. Clin Transl Immunology. 2020. PMID: 32994998 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
