Functionally asymmetric motor neurons contribute to coordinating locomotion of Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 30204083
- PMCID: PMC6173582
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.34997
Functionally asymmetric motor neurons contribute to coordinating locomotion of Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
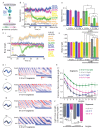
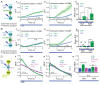
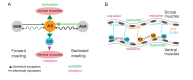
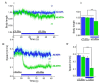
Locomotion circuits developed in simple animals, and circuit motifs further evolved in higher animals. To understand locomotion circuit motifs, they must be characterized in many models. The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans possesses one of the best-studied circuits for undulatory movement. Yet, for 1/6th of the cholinergic motor neurons (MNs), the AS MNs, functional information is unavailable. Ventral nerve cord (VNC) MNs coordinate undulations, in small circuits of complementary neurons innervating opposing muscles. AS MNs differ, as they innervate muscles and other MNs asymmetrically, without complementary partners. We characterized AS MNs by optogenetic, behavioral and imaging analyses. They generate asymmetric muscle activation, enabling navigation, and contribute to coordination of dorso-ventral undulation as well as anterio-posterior bending wave propagation. AS MN activity correlated with forward and backward locomotion, and they functionally connect to premotor interneurons (PINs) for both locomotion regimes. Electrical feedback from AS MNs via gap junctions may affect only backward PINs.
Keywords: C. elegans; Ca2+ imaging; behavioral analysis; gap junctions; locomotor circuit; neuroscience; optogenetics.
© 2018, Tolstenkov et al.
Conflict of interest statement
OT, PV, WS, OB, TG, AB, AG No competing interests declared
Figures

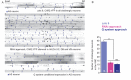
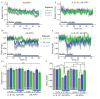
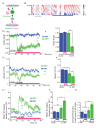


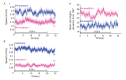




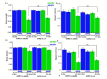
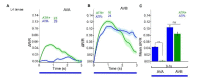
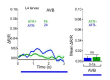
References
-
- Akerboom J, Carreras Calderón N, Tian L, Wabnig S, Prigge M, Tolö J, Gordus A, Orger MB, Severi KE, Macklin JJ, Patel R, Pulver SR, Wardill TJ, Fischer E, Schüler C, Chen TW, Sarkisyan KS, Marvin JS, Bargmann CI, Kim DS, Kügler S, Lagnado L, Hegemann P, Gottschalk A, Schreiter ER, Looger LL. Genetically encoded calcium indicators for multi-color neural activity imaging and combination with optogenetics. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience. 2013;6:1–29. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2013.00002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bergs A, Schultheis C, Fischer E, Tsunoda SP, Erbguth K, Husson SJ, Govorunova E, Spudich JL, Nagel G, Gottschalk A, Liewald JF. Rhodopsin optogenetic toolbox v2.0 for light-sensitive excitation and inhibition in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0191802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191802. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

