Patient-mediated interventions to improve professional practice
- PMID: 30204235
- PMCID: PMC6513263
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012472.pub2
Patient-mediated interventions to improve professional practice
Abstract
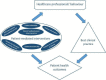
Background: Healthcare professionals are important contributors to healthcare quality and patient safety, but their performance does not always follow recommended clinical practice. There are many approaches to influencing practice among healthcare professionals. These approaches include audit and feedback, reminders, educational materials, educational outreach visits, educational meetings or conferences, use of local opinion leaders, financial incentives, and organisational interventions. In this review, we evaluated the effectiveness of patient-mediated interventions. These interventions are aimed at changing the performance of healthcare professionals through interactions with patients, or through information provided by or to patients. Examples of patient-mediated interventions include 1) patient-reported health information, 2) patient information, 3) patient education, 4) patient feedback about clinical practice, 5) patient decision aids, 6) patients, or patient representatives, being members of a committee or board, and 7) patient-led training or education of healthcare professionals.
Objectives: To assess the effectiveness of patient-mediated interventions on healthcare professionals' performance (adherence to clinical practice guidelines or recommendations for clinical practice).
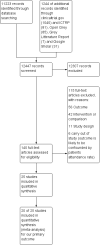
Search methods: We searched MEDLINE, Ovid in March 2018, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) in March 2017, and ClinicalTrials.gov and the International Clinical Trials Registry (ICTRP) in September 2017, and OpenGrey, the Grey Literature Report and Google Scholar in October 2017. We also screened the reference lists of included studies and conducted cited reference searches for all included studies in October 2017.
Selection criteria: Randomised studies comparing patient-mediated interventions to either usual care or other interventions to improve professional practice.
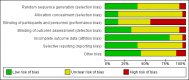
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed studies for inclusion, extracted data and assessed risk of bias. We calculated the risk ratio (RR) for dichotomous outcomes using Mantel-Haenszel statistics and the random-effects model. For continuous outcomes, we calculated the mean difference (MD) using inverse variance statistics. Two review authors independently assessed the certainty of the evidence (GRADE).
Main results: We included 25 studies with a total of 12,268 patients. The number of healthcare professionals included in the studies ranged from 12 to 167 where this was reported. The included studies evaluated four types of patient-mediated interventions: 1) patient-reported health information interventions (for instance information obtained from patients about patients' own health, concerns or needs before a clinical encounter), 2) patient information interventions (for instance, where patients are informed about, or reminded to attend recommended care), 3) patient education interventions (intended to increase patients' knowledge about their condition and options of care, for instance), and 4) patient decision aids (where the patient is provided with information about treatment options including risks and benefits). For each type of patient-mediated intervention a separate meta-analysis was produced.Patient-reported health information interventions probably improve healthcare professionals' adherence to recommended clinical practice (moderate-certainty evidence). We found that for every 100 patients consulted or treated, 26 (95% CI 23 to 30) are in accordance with recommended clinical practice compared to 17 per 100 in the comparison group (no intervention or usual care). We are uncertain about the effect of patient-reported health information interventions on desirable patient health outcomes and patient satisfaction (very low-certainty evidence). Undesirable patient health outcomes and adverse events were not reported in the included studies and resource use was poorly reported.Patient information interventions may improve healthcare professionals' adherence to recommended clinical practice (low-certainty evidence). We found that for every 100 patients consulted or treated, 32 (95% CI 24 to 42) are in accordance with recommended clinical practice compared to 20 per 100 in the comparison group (no intervention or usual care). Patient information interventions may have little or no effect on desirable patient health outcomes and patient satisfaction (low-certainty evidence). We are uncertain about the effect of patient information interventions on undesirable patient health outcomes because the certainty of the evidence is very low. Adverse events and resource use were not reported in the included studies.Patient education interventions probably improve healthcare professionals' adherence to recommended clinical practice (moderate-certainty evidence). We found that for every 100 patients consulted or treated, 46 (95% CI 39 to 54) are in accordance with recommended clinical practice compared to 35 per 100 in the comparison group (no intervention or usual care). Patient education interventions may slightly increase the number of patients with desirable health outcomes (low-certainty evidence). Undesirable patient health outcomes, patient satisfaction, adverse events and resource use were not reported in the included studies.Patient decision aid interventions may have little or no effect on healthcare professionals' adherence to recommended clinical practice (low-certainty evidence). We found that for every 100 patients consulted or treated, 32 (95% CI 24 to 43) are in accordance with recommended clinical practice compared to 37 per 100 in the comparison group (usual care). Patient health outcomes, patient satisfaction, adverse events and resource use were not reported in the included studies.
Authors' conclusions: We found that two types of patient-mediated interventions, patient-reported health information and patient education, probably improve professional practice by increasing healthcare professionals' adherence to recommended clinical practice (moderate-certainty evidence). We consider the effect to be small to moderate. Other patient-mediated interventions, such as patient information may also improve professional practice (low-certainty evidence). Patient decision aids may make little or no difference to the number of healthcare professionals' adhering to recommended clinical practice (low-certainty evidence).The impact of these interventions on patient health and satisfaction, adverse events and resource use, is more uncertain mostly due to very low certainty evidence or lack of evidence.
Conflict of interest statement
Marita S Fønhus: none known.
Therese K Dalsbø: none known.
Marit Johansen: none known.
Atle Fretheim: none known.
Helge Skirbekk: none known.
Signe A Flottorp: none known.
Figures
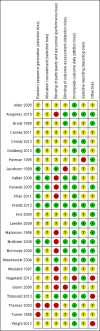
Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Alder 2005 {published data only}
-
- Alder SC, Trunnell EP, White GL, Lyon JLJ, Reading JP, Magill MK. Reducing parental demand for antibiotics by promoting communication skills. American Journal of Health Education 2005;363(3):132‐9.
Aragones 2010 {published data only}
Brody 1990 {published data only}
-
- Brody DS, Lerman CE, Wolfson HG, Caputo GC. Improvement in physicians' counseling of patients with mental health problems. Archives of Internal Medicine 1990;150(5):993‐8. - PubMed
Caskey 2011 {published data only}
-
- Caskey R, Weiner S, Gerber B. Exam‐room based education to influence vaccination behavior among veteran patients in a primary care setting. Journal of General Internal Medicine 2011;26:S271.
Christy 2013 {published data only}
Goldberg 2012 {published data only}
-
- Goldberg EM, Laskowski‐Kos U, Wu D, Gutierrez J, Bilderback A, Okelo S, et al. Can the pediatric asthma control and communication instrument (PACCI) be used in the ED to improve clinicians' assessment of asthma control?. Academic Emergency Medicine. Conference: 2012 Annual Meeting of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine. Vol. Conference Publication: (var.pagings): 19, issue s1:S348.
Herman 1995 {published data only}
-
- Herman CJ, Speroff T, Cebul RD. Improving compliance with breast cancer screening in older women. Results of a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 1995;155(7):717‐22. - PubMed
Jacobson 1999 {published data only}
-
- Jacobson TA, Thomas DM, Morton FJ, Offutt G, Shevlin J, Ray S. Use of a low‐literacy patient education tool to enhance pneumococcal vaccination rates. A randomized controlled trial. Jama 1999;282(7):646‐50. - PubMed
Kattan 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kattan M, Crain EF, Steinbach S, Visness CM, Walter M, Stout JW, et al. A randomized clinical trial of clinician feedback to improve quality of care for inner‐city children with asthma. Pediatrics 2006;117(6):e1095‐103. - PubMed
Kenealy 2005 {published and unpublished data}
Khan 2011 {published data only}
Kravitz 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kravitz RL, Tancredi DJ, Jerant A, Saito N, Street RL, Grennan T, et al. Influence of patient coaching on analgesic treatment adjustment: secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial. J Pain Symptom Manage 2012;43(5):874‐84. - PubMed
Krol 2004 {published data only}
-
- Krol N, Wensing M, Haaijer‐Ruskamp F, Muris JW, Numans ME, Schattenberg G, et al. Patient‐directed strategy to reduce prescribing for patients with dyspepsia in general practice: a randomized trial. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2004;19(8):917‐22. - PubMed
Leveille 2009 {published data only}
-
- Leveille SG, Huang A, Tsai SB, Allen M, Weingart SN, Iezzoni LI. Health coaching via an internet portal for primary care patients with chronic conditions: a randomized controlled trial. Medical Care 2009;47(1):41‐7. - PubMed
Mazonson 1996 {published data only}
-
- Mazonson PD, Mathias SD, Fifer SK, Buesching DP, Malek P, Patrick DL. The mental health patient profile: does it change primary care physicians' practice patterns?. Journalof the American Board of Family Practice/ American Board of Family Practice 1996;9(5):336–45. - PubMed
McAlister 2005 {published data only}
McKinstry 2006 {published data only}
Miaskowski 2004 {published data only}
-
- Miaskowski C, Dodd M, West C, Schumacher K, Paul SM, Tripathy D, et al. Randomized clinical trial of the effectiveness of a self‐care intervention to improve cancer pain management. Journal of Clinical Oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2004;22(9):1713‐20. - PubMed
Mouland 1997 {published data only}
-
- Mouland G. A letter to benzodiazepine users‐‐an efficient way to reduce the prescription. Tidsskrift for den Norske lægeforening 1997;117(21):3097‐100. - PubMed
Nagykaldi 2012 {published data only}
-
- Nagykaldi Z, Aspy CB, Chou A, Mold JW. Impact of a Wellness Portal on the delivery of patient‐centered preventive care. Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine 2012;25(2):158‐67. - PubMed
Quinn 2008 {published data only}
-
- Quinn CC, Clough SS, Minor JM, Lender D, Okafor MC, Gruber‐Baldini A. WellDoc mobile diabetes management randomized controlled trial: change in clinical and behavioral outcomes and patient and physician satisfaction. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics 2008;10(3):160‐8. - PubMed
Thiboutot 2013 {published data only}
Thomas 2003 {published data only}
-
- Thomas DM, Ray SM, Morton FJ, Drew JS, Offutt G, Whitney CG, et al. Patient education strategies to improve pneumococcal vaccination rates: randomized trial. Journal of Investigative Medicine 2003;51(3):141‐8. - PubMed
Turner 1990 {published data only}
-
- Turner RC, Waivers LE, O'Brien K. The effect of patient‐carried reminder cards on the performance of health maintenance measures. Archives of Internal Medicine 1990;150(3):645‐7. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Adams 2014 {published data only}
-
- Adams WG, Phillips BD, Bacic JD, Walsh KE, Shanahan CW, Paasche‐Orlow MK. Automated conversation system before pediatric primary care visits: a randomized trial. Pediatrics 2014;134(3):e691‐99. - PubMed
Alexander 2011 {published data only}
Altiner 2007 {published data only}
-
- Altiner A, Brockmann S, Sielk M, Wilm S, Wegscheider K, Abholz HH. Reducing antibiotic prescriptions for acute cough by motivating GPs to change their attitudes to communication and empowering patients: a cluster‐randomized intervention study. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2007;60(3):638‐44. - PubMed
Amble 2015 {published data only}
-
- Amble I, Gude T, Stubdal S, Andersen BJ, Wampold BE. The effect of implementing the Outcome Questionnaire‐45.2 feedback system in Norway: A multisite randomized clinical trial in a naturalistic setting. Psychotherapy Research 2015;25(6):669‐77. - PubMed
Anderson 2004 {published data only}
-
- Anderson KO, Mendoza TR, Payne R, Valero V, Palos GR, Nazario A, et al. Pain education for underserved minority cancer patients: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2004;22(24):4918‐25. - PubMed
Ansari 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ansari M, Shlipak MG, Heidenreich PA, Ostaeyen D, Pohl EC, Browner WS, et al. Improving guideline adherence: a randomized trial evaluating strategies to increase beta‐blocker use in heart failure. Circulation 2003;107(22):2799‐804. - PubMed
Atherton‐Naji 2001 {published data only}
-
- Atherton‐Naji A, Hamilton R, Riddle W, Naji S. Improving adherence to antidepressant drug treatment in primary care: A feasibility study for a randomized controlled trial of education intervention. Primary Care Psychiatry 2001;7(2):61‐7.
Barr 2001 {published data only}
-
- Barr JK, Franks AL, Lee NC, Antonucci DM, Rifkind S, Schachter M. A randomized intervention to improve ongoing participation in mammography. American Journal of Managed Care 2001;7(9):887‐94. - PubMed
Basch 1999 {published data only}
Becker 1989 {published data only}
-
- Becker D M, Gomez E B, Kaiser D L, Yoshihasi A, Hodge R H Jr. Improving preventive care at a medical clinic: how can the patient help?. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 1989;5(6):353‐9. - PubMed
Bessette 2011 {published data only}
-
- Bessette L, Davison KS, Jean S, Roy S, Ste‐Marie LG, Brown JP. The impact of two educational interventions on osteoporosis diagnosis and treatment after fragility fracture:a population‐based randomized controlled trial. Osteoporos International 2011;22(12):2963‐72. - PubMed
Bickman 2011 {published data only}
-
- Bickman L, Kelley SD, Breda C, Andrade AR, Riemer M. Effects of routine feedback to clinicians on mental health outcomes of youths: results of a randomized trial. Psychiatric Services 2011;62(12):1423‐9. - PubMed
Bird 1990 {published data only}
-
- Bird JA, McPhee SJ, Jenkins C, Fordham D. Three strategies to promote cancer screening. How feasible is wide‐scale implementation?. Medical Care 1990;28(11):1005‐12. - PubMed
Bloomfield 2005 {published data only}
-
- Bloomfield HE, Nelson DB, Ryn M, Neil BJ, Koets NJ, Basile JN, et al. A trial of education, prompts, and opinion leaders to improve prescription of lipid modifying therapy by primary care physicians for patients with ischemic heart disease. Quality & Safety in Health Care 2005;14(4):258‐63. - PMC - PubMed
Branch 1999 {published data only}
-
- Branch VK, Graves G, Hanczyc M, Lipsky PE. The utility of trained arthritis patient educators in the evaluation and improvement of musculoskeletal examination skills of physicians in training. Arthritis Care and Research : the official journal of the Arthritis Health Professions Association 1999;12(1):61‐9. - PubMed
Brinkman 2007 {published data only}
-
- Brinkman WB, Geraghty SR, Lanphear BP, Khoury JC, Gonzalez del Rey JA, Dewitt TG, et al. Effect of multisource feedback on resident communication skills and professionalism: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2007;161(1):44‐9. - PubMed
Brodey 2005 {published data only}
-
- Brodey BB, Cuffel B, McCulloch J, Tani S, Maruish M, Brodey I, et al. The acceptability and effectiveness of patient‐reported assessments and feedback in a managed behavioral healthcare setting. American Journal of Managed Care 2005;11(12):774‐80. - PubMed
Burack 1994 {published data only}
-
- Burack RC, Gimotty PA, George J, Stengle W, Warbasse L, Moncrease A. Promoting screening mammography in inner‐city settings: a randomized controlled trial of computerized reminders as a component of a program to facilitate mammography. Medical Care 1994;32(6):609‐24. - PubMed
Burack 1996 {published data only}
-
- Burack RC, Gimotty PA, George J, Simon MS, Dews P, Moncrease A. The effect of patient and physician reminders on use of screening mammography in a health maintenance organization. Results of a randomized controlled trial. Cancer 1996;78(8):1708‐21. - PubMed
Burack 1998 {published data only}
-
- Burack RC, Gimotty PA, George J, McBride S, Moncrease A, Simon MS, Dews P, Coombs J. How reminders given to patients and physicians affected pap smear use in a health maintenance organization: results of a randomized controlled trial. Cancer 1998;82(12):2391‐400. - PubMed
Burack 2003 {published data only}
-
- Burack RC, Gimotty PA, Simon M, Moncrease A, Dews P. The effect of adding Pap smear information to a mammography reminder system in an HMO: results of randomized controlled trial. Preventive Medicine 2003;36(5):547‐54. - PubMed
Campbell 1997 {published data only}
-
- Campbell E, Peterkin D, Abbott R, Rogers J. Encouraging underscreened women to have cervical cancer screening: the effectiveness of a computer strategy. Preventive medicine 1997;26(6):801‐7. - PubMed
Chang 2012 {published data only}
-
- Chang TE, Jing Y, Yeung AS, Brenneman SK, Kalsekar I, Hebden T, et al. Effect of communicating depression severity on physician prescribing patterns: findings from the Clinical Outcomes in MEasurement‐based Treatment (COMET) trial. General Hospital Psychiatry 2012;34(2):105‐12. - PubMed
Chodosh 2015 {published data only}
-
- Chodosh J, Colaiaco BA, Connor KI, Cope DW, Liu H, Ganz DA, et al. Dementia care management in an underserved community: the comparative effectiveness of two different approaches. Journal of Aging & Health 2015;27(5):864‐93. - PubMed
Chou 2011 {published data only}
-
- Chou PL, Lin CC. A pain education programme to improve patient satisfaction with cancer pain management: a randomised control trial. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2011;20(13‐4):1858‐69. - PubMed
Clementz 1990 {published data only}
-
- Clementz GL, Aldag JC, Gladfelter TT, Barclay AM, Brooks HF. A randomized study of cancer screening in a family practice setting using a recall model. Journal of Family Practice 1990;30(5):537‐41. - PubMed
Clever 2006 {published data only}
-
- Clever SL, Ford D E, Rubenstein LV, Rost KM, Meredith L‐S, Sherbourne CD, et al. Primary care patients' involvement in decision‐making is associated with improvement in depression. Medical Care 2006;44(5):398‐405. - PubMed
Clover 1992 {published data only}
-
- Clover KA, Redman S, Forbes JF, Sanson‐Fisher RW, Dickinson JA. Promotion of attendance for mammographic screening through general practice: a randomised trial of two strategies. Medical Journal of Australia 1992;156(2):91‐4. - PubMed
Cohen‐Cline 2014 {published data only}
-
- Cohen‐Cline H, Wernli KJ, Bradford SC, Boles‐Hall M, Grossman DC. Use of interactive voice response to improve colorectal cancer screening. Medical Care 2014;52(6):496‐9. - PubMed
Cooper 2011 {published data only}
Cooper 2013 {published data only}
-
- Cooper LA, Ghods Dinoso BK, Ford DE, Roter D L, Primm AB, Larson SM, et al. Comparative effectiveness of standard versus patient‐centered collaborative care interventions for depression among African Americans in primary care settings: the BRIDGE Study. Health Services Research 2013;48(1):150‐74. - PMC - PubMed
Corson 2011 {published data only}
-
- Corson K, Doak MN, Denneson L, Crutchfield M, Soleck G, Dickinson KC, et al. Primary care clinician adherence to guidelines for the management of chronic musculoskeletal pain: results from the study of the effectiveness of a collaborative approach to pain. Pain Medicine 2011;12(10):1490‐501. - PubMed
Costanza 2007 {published data only}
-
- Costanza ME, Luckmann R, Stoddard AM, White MJ, Stark JR, Avrunin JS, et al. Using tailored telephone counseling to accelerate the adoption of colorectal cancer screening. Cancer Detection & Prevention 2007;31(3):191‐8. - PubMed
Datto 2003 {published data only}
-
- Datto CJ, Thompson R, Horowitz D, Disbot M, Oslin DW. The pilot study of a telephone disease management program for depression. General Hospital Psychiatry 2003;25(3):169‐77. - PubMed
Deeb 1988 {published data only}
-
- Deeb LC, Pettijohn FP, Shirah J K, Freeman G. Interventions among primary‐care practitioners to improve care for preventable complications of diabetes. Diabetes Care 1988;11(3):275‐80. - PubMed
Dietrich 2013 {published data only}
Dolan 2002 {published data only}
-
- Dolan JG, Frisina S. Randomized controlled trial of a patient decision aid for colorectal cancer screening. Medical Decision Making : an international journal of the Society for Medical Decision Making 2002;22(2):125‐39. - PubMed
Early 2015 {published data only}
-
- Early F, Everden AJ, O'Brien CM, Fagan PL, Fuld JP. Patient agenda setting in respiratory outpatients: A randomized controlled trial. Chronic Respiratory Disease 2015;12(4):347‐56. - PubMed
Echeverry 2003 {published data only}
Feder 1999 {published data only}
Finlay 1999 {published data only}
-
- Finlay IG, Wyatt P. Randomised cross‐over study of patient‐held records in oncology and palliative care. Lancet (London, England) 1999;353(9152):558‐9. - PubMed
Fisher 2011 {published data only}
Fleisher 1999 {published data only}
-
- Fleisher LA, Mark L, Lam J, Pearlman A, Fisher Q, Snyder DS, et al. Disseminating information using an anesthesiology consultant report: impact on patient perceptions of quality of care. Journal of Clinical anesthesia 1999;11(5):380‐5. - PubMed
Flottorp 2002 {published data only}
Fluckiger 2012 {published data only}
-
- Fluckiger C, Re AC, Wampold BE, Znoj H, Caspar F, Jorg U. Valuing clients' perspective and the effects on the therapeutic alliance: a randomized controlled study of an adjunctive instruction. Journal of Counseling Psychology 2012;59(1):18‐26. - PubMed
Förberg 2017 {published data only}
Fortuna 2014 {published data only}
Gabbay 2012 {published data only}
Galliher 2010 {published data only}
Garcia 2013 {published data only}
-
- Garcia BH, Giverhaug T, Utnes J, Smabrekke L. A follow‐up program for patients with established coronary heart disease led by a clinical pharmacist: A randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy 2013;35(6):1255‐6.
Garcia 2015 {published data only}
Gersch 2014 {published data only}
-
- Gersch C, Ebel M. [Both patients and physicians benefit from internet‐based communication (APIKAP study)]. MMW Fortschritte der Medizin 2014;156 Suppl 2:31‐8. - PubMed
Ghadieh 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ghadieh AS, Hamadeh GN, Mahmassani DM, Lakkis NA. The effect of various types of patients' reminders on the uptake of pneumococcal vaccine in adults: A randomized controlled trial. Vaccine 2015;33(43):5868‐72. - PubMed
Ginson 2000 {published data only}
-
- Ginson SH, Malmberg C, French DJ. Impact on vaccination rates of a pharmacist‐initiated influenza and pneumococcal vaccination program. Canadian Journal of Hospital Pharmacy 2000;53(4):270‐5.
Gooding 2012 {published data only}
-
- Gooding HC, Blood EA, Sharma N. An educational intervention to increase internists' confidence with and provision of preventive services to adolescents and young adults. Teaching & Learning in Medicine 2012;24(4):321‐6. - PubMed
Grace 2005 {published data only}
Greco 2001 {published data only}
-
- Greco M, Brownlea A, McGovern J. Impact of patient feedback on the interpersonal skills of general practice registrars: results of a longitudinal study. Medical Eeducation 2001;35(8):748‐56. - PubMed
Haskard 2008 {published data only}
-
- Haskard KB, Williams SL, DiMatteo MR, Rosenthal R, White MK, Goldstein MG. Physician and patient communication training in primary care: effects on participation and satisfaction.[Erratum appears in Health Psychol. 2009 Mar;28(2):263]. Health Psychology 2008;27(5):513‐22. - PubMed
Hornberger 1997 {published data only}
Jager 2017 {published data only}
-
- Jager C, Freund T, Steinhauser J, Stock C, Krisam J, Kaufmann‐Kolle P, et al. Impact of a tailored program on the implementation of evidence‐based recommendations for multimorbid patients with polypharmacy in primary care practices‐results of a cluster‐randomized controlled trial. Implementation Science 2017;12(1):8. - PMC - PubMed
Katz 2011 {published data only}
Kinugasa 2014 {published data only}
Kravitz 2005 {published data only}
Lafata 2007 {published data only}
Lawton 2017 {published data only}
Levy 2013 {published data only}
-
- Levy BT, Xu Y, Daly JM, Ely JW. A randomized controlled trial to improve colon cancer screening in rural family medicine: an Iowa Research Network (IRENE) study. Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine: JABFM 2013;26(5):486‐97. - PubMed
Linder 2009 {published data only}
Little 2004 {published data only}
-
- Little P, Dorward M, Warner G, Moore M, Stephens K, Senior J, et al. Randomised controlled trial of effect of leaflets to empower patients in consultations in primary care. BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 2004;328(7437):10.1136/bmj.37999.716157.44. [DOI: 10.1136/bmj.37999.716157.44] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Liu 2016 {published data only}
Lynch 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lynch FL, Whitlock EP, Valanis BG, Smith SK. Cost‐effectiveness of a tailored intervention to increase screening in HMO women overdue for Pap test and mammography services. Preventive Medicine 2004;38(4):403‐11. - PubMed
Manfredi 1998 {published data only}
-
- Manfredi C, Czaja R, Freels S, Trubitt M, Warnecke R, Lacey L. Prescribe for health. Improving cancer screening in physician practices serving low‐income and minority populations. Archives of Family Medicine 1998;7(4):329‐37. - PubMed
Marshall 2016 {published data only}
Marteau 2010 {published data only}
Menon 2011 {published data only}
Michalopoulou 2010 {published data only}
-
- Michalopoulou G, Falzarano P, Arfken C, Rosenberg D. Implementing Ask Me 3 to improve African American patient satisfaction and perceptions of physician cultural competency. Journal of Cultural Diversity 2010;17(2):62‐7. - PubMed
Mitchell 2005 {published data only}
Mohler 1995 {published data only}
-
- Mohler PJ. Enhancing compliance with screening mammography recommendations: a clinical trial in a primary care office. Family Medicine 1995;27(2):117‐21. - PubMed
Myers 2007 {published data only}
-
- Myers RE, Sifri R, Hyslop T, Rosenthal M, Vernon SW, Cocroft J, et al. A randomized controlled trial of the impact of targeted and tailored interventions on colorectal cancer screening. Cancer 2007;110(9):2083‐91. - PubMed
Myers 2008 {published data only}
-
- Myers RE, Hyslop T, Sifri R, Bittner‐Fagan H, Katurakes NC, Cocroft J, et al. Tailored navigation in colorectal cancer screening. Medical Care 2008;46(9 Suppl 1):S123‐31. - PubMed
Myers 2011 {published data only}
-
- Myers RE, Daskalakis C, Kunkel EJ, Cocroft J R, Riggio JM, Capkin M, et al. Mediated decision support in prostate cancer screening: a randomized controlled trial of decision counseling. Patient Education & Counseling 2011;83(2):240‐6. - PubMed
O'Connor 2009 {published data only}
Olsson 2012 {published data only}
Ornstein 1991 {published data only}
-
- Ornstein SM, Garr DR, Jenkins RG, Rust PF, Arnon A. Computer‐generated physician and patient reminders. Tools to improve population adherence to selected preventive services. Journal of Family Practice 1991;32(1):82‐90. - PubMed
Osborn 2010 {published data only}
-
- Osborn DP, Nazareth I, Wright CA, King MB. Impact of a nurse‐led intervention to improve screening for cardiovascular risk factors in people with severe mental illnesses. Phase‐two cluster randomised feasibility trial of community mental health teams. BMC Health Services Research 2010;10:61. - PMC - PubMed
Osman 1994 {published data only}
Osman 2002 {published data only}
Persell 2008 {published data only}
-
- Persell SD, Denecke‐Dattalo TA, Dunham DP, Baker DW. Patient‐directed intervention versus clinician reminders alone to improve aspirin use in diabetes: a cluster randomized trial. Joint Commission Journal on Quality & Patient Safety 2008;34(2):98‐105. - PubMed
Porter 2006 {published data only}
-
- Porter SC, Forbes P, Feldman HA, Goldmann DA. Impact of patient‐centered decision support on quality of asthma care in the emergency department. Pediatrics 2006;117(1):e33‐42. - PubMed
Raisch 1999 {published data only}
Reinders 2010 {published data only}
-
- Reinders ME, Blankenstein AH, Horst HE, Knol DL, Schoonheim PL, Marwijk HW. Does patient feedback improve the consultation skills of general practice trainees? A controlled trial. Medical Education 2010;44(2):156‐64. - PubMed
Rise 2012 {published data only}
Robling 2012 {published data only}
-
- Robling M, McNamara R, Bennert K, Butler CC, Channon S, Cohen D, et al. The effect of the Talking Diabetes consulting skills intervention on glycaemic control and quality of life in children with type 1 diabetes: cluster randomised controlled trial (DEPICTED study). BMJ 2012;344:e2359. - PMC - PubMed
Roland 1989 {published data only}
Rosenthal 2005 {published data only}
-
- Rosenthal MS, Lannon CM, Stuart JM, Brown L, Miller WC, Margolis PA. A randomized trial of practice‐based education to improve delivery systems for anticipatory guidance. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2005;159(5):456‐63. - PubMed
Rosser 1991 {published data only}
Rubenstein 1995 {published data only}
-
- Rubenstein LV, McCoy JM, Cope DW, Barrett PA, Hirsch SH, Messer KS, et al. Improving patient quality of life with feedback to physicians about functional status. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1995;10(11):607‐14. - PubMed
Sherrard 2015 {published data only}
-
- Sherrard H, Duchesne L, Wells G, Kearns SA, Struthers C. Using interactive voice response to improve disease management and compliance with acute coronary syndrome best practice guidelines: A randomized controlled trial. Canadian Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing 2015;25(1):10‐5. - PubMed
Simon 2012 {published data only}
-
- Simon W, Lambert MJ, Harris MW, Busath G, Vazquez A. Providing patient progress information and clinical support tools to therapists: effects on patients at risk of treatment failure. Psychotherapy Research 2012;22(6):638‐47. - PubMed
Smeele 1999 {published data only}
Smit 2005 {published data only}
-
- Smit A, Tiemens BG, Ormel J, Kluiter H, Jenner JA, Meer K, et al. Enhanced treatment for depression in primary care: First year results on compliance, self‐efficacy, the use of antidepressants and contacts with the primary care physician. Primary Care & Community Psychiatry 2005;10(2):39‐49.
Solomon 2007 {published data only}
Sonnichsen 2010 {published data only}
Spahr 2006 {published data only}
-
- Spahr CD, Flugstad NA, Brousseau DC. The impact of a brief expectation survey on parental satisfaction in the pediatric emergency department. Academic Emergency Medicine 2006;13(12):1280‐7. - PubMed
Spaic 2013 {published data only}
-
- Spaic T, Mahon J L, Hramiak I, Byers N, Evans K, Robinson T, et al. Multicentre randomized controlled trial of structured transition on diabetes care management compared to standard diabetes care in adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes (Transition Trial). BMC Pediatrics 2013;13:163. - PMC - PubMed
Thapar 2002 {published data only}
-
- Thapar A, Jacoby A, Richens A, Russell I, Roberts C, Porter E, et al. A pragmatic randomised controlled trial of a prompt and reminder card in the care of people with epilepsy. British Journal of General Practice : the journal of the Royal College of General Practitioner 2002;52(475):93‐8. - PMC - PubMed
Valanis 2002 {published data only}
-
- Valanis BG, Glasgow RE, Mullooly J, Vogt TM, Whitlock EP, Boles SM, et al. Screening HMO women overdue for both mammograms and pap tests. Preventive Medicine 2002;34(1):40‐50. - PubMed
Vallès 2002 {published data only}
-
- Vallès JA, Barreiro M, Cereza G, Ferro JJ, Martínez MJ, Cucurull E, et al. [Acceptance of generic prescribing in general practice: effect of patient education and reference prices]. Gaceta Sanitaria / S.E.S.P.A.S 2002;16(6):505‐10. - PubMed
Vallès 2003 {published data only}
-
- Vallès JA, Barreiro M, Cereza G, Ferro JJ, Martínez MJ, Escribà JM, et al. A prospective multicenter study of the effect of patient education on acceptability of generic prescribing in general practice. Health policy (Amsterdam, Netherlands) 2003;65(3):269‐75. - PubMed
Vickrey 2006 {published data only}
-
- Vickrey BG, Mittman BS, Connor KI, Pearson ML, Della Penna RD, Ganiats TG, et al. The effect of a disease management intervention on quality and outcomes of dementia care: a randomized, controlled trial.[Summary for patients in Ann Intern Med. 2006 Nov 21;145(10):I31; PMID: 17116913]. Annals of Internal Medicine 2006;145(10):713‐26. - PubMed
Vingerhoets 2001 {published data only}
Wasson 1999 {published data only}
-
- Wasson JH, Stukel TA, Weiss JE, Hays RD, Jette AM, Nelson EC. A randomized trial of the use of patient self‐assessment data to improve community practices. Effective Clinical Practice 1999;2(1):1‐10. - PubMed
Wensing 2003 {published data only}
-
- Wensing M, Vingerhoets E, Grol R. Feedback based on patient evaluations: a tool for quality improvement?. Patient Education and Counseling 2003;51(2):149‐53. - PubMed
Wilson 1993 {published data only}
-
- Wilson SR, Scamagas P, German DF, Hughes GW, Lulla S, Coss S, et al. A controlled trial of two forms of self‐management education for adults with asthma. American Journal of Medicine 1993;94(6):564‐76. - PubMed
Wynia 2010 {published data only}
Zermansky 2001 {published data only}
References to ongoing studies
NCT01904656 {published data only}
-
- NCT01904656. CBPR Strategies to Increase colorectal cancer screening in Ohio Appalachia. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01904656 (date accessed 18th of Sept. 2017).
NCT02686775 {published data only}
-
- NCT02686775. The PACO Project: A clinical study of a PAtient COach program in vulnerable lung cancer patients (PACO). https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02686775 (date accessed 18th of Sept. 2017).
Additional references
ABDN 2015
-
- University of Aberdeen. Research tools. Database of intra‐correlation coefficients (ICCs). www.abdn.ac.uk/hsru/research/research‐tools/ (accessed prior to 7 December 2016).
Anderson 2017
Arditi 2017
Attridge 2014
Bennett 2016
Clarkesmith 2017
Covidence
-
- Covidence systematic review software, Veritas Health Innovation, Melbourne, Australia. Covidence systematic review software, Veritas Health Innovation, Melbourne, Australia. Available at www.covidence.org.
Davis 1995
-
- Davis DA, Thomson MA, Oxman AD, Haynes RB. Changing physician performance. A systematic review of the effect of continuing medical education strategies. JAMA 1995;274(9):700‐5. - PubMed
Davis 2012a
-
- Davis RE, Sevdalis N, Vincent CA. Patient involvement in patient safety: the health‐care professionals' perspective. Journal of Patient Safety 2012;8(4):182‐8. - PubMed
Davis 2012b
-
- Davis RE, Pinto A, Sevdalis N, Vincent C, Massey R, Darzi A. Patients' and health care professionals' attitudes towards the PINK patient safety video. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice 2012;18(4):848‐53. - PubMed
Dwamena 2012
Egger 1997
EPOC 2017a
-
- Cochrane Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). Data extraction and management. EPOC Resources for review authors, 2017. Available from epoc.cochrane.org/epoc‐specific‐resources‐review‐authors.
EPOC 2017b
-
- Cochrane Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). Suggested risk of bias criteria for EPOC reviews. EPOC Resources for review authors, 2017. Available from epoc.cochrane.org/epoc‐specific‐resources‐review‐authors.
EPOC 2017c
-
- Cochrane Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). EPOC worksheets for preparing a Summary of Findings (SoF) table using GRADE. EPOC resources for review authors, 2017. Available from epoc.cochrane.org/epoc‐specific‐resources‐review‐authors.
EPOC 2017d
-
- Cochrane Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). Reporting the effects of an intervention in EPOC reviews. EPOC Resources for review authors, 2017. Available at: http://epoc.cochrane.org/resources/epoc‐resources‐review‐authors.
Flodgren 2011a
Flodgren 2011b
-
- Flodgren G, Eccles MP, Shepperd S, Scott A, Parmelli E, Beyer FR. An overview of reviews evaluating the effectiveness of financial incentives in changing healthcare professional behaviours and patient outcomes. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011, Issue 7. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009255] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Flodgren 2016
Forsetlund 2009
Fryer 2016
Gagliardi 2016
Giguère 2012
GRADEpro GDT 2015 [Computer program]
-
- GRADE Working Group, McMaster University. GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool. Version accessed prior to 7 December 2016. Hamilton (ON): GRADE Working Group, McMaster University, 2015.
Grimshaw 2004
-
- Grimshaw JM, Thomas RE, Maclennan G, Fraser C, Ramsay CR, Vale L, et al. Effectiveness and efficiency of guideline dissemination and implementation strategies. Health Technology Assessment 2004;8:iii‐72. - PubMed
Grol 2003
-
- Grol R, Grimshaw J. From best evidence to best practice: effective implementation of change in patients' care. Lancet 2003;362(9391):1225‐30. - PubMed
Harbord 2006
-
- Harbord RM, Egger M, Sterne JA. A modified test for small‐study effects in meta ‐analyses of controlled trials with binary endpoints. Statistics in Medicine 2006;25:344‐57. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Hrisos 2013
Ivers 2012
Kelly 2018
Khalil 2017
Kroon 2014
Lenferink 2017
-
- Lenferink A, Brusse‐Keizer M, Valk PDLPM, Frith PA, Zwerink M, Monninkhof EM, vet al. Self‐management interventions including action plans for exacerbations versus usual care in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2017, Issue 8. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011682.pub2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Luszczynska 2007
-
- Luszczynska A, Gunson KSE. Predictors of asking medical personnel about handwashing: The moderating role of patients’ age and MRSA infection status. Patient Education and Counseling 2007;68(1):79‐85. - PubMed
Légaré 2014
McBain 2016
McCallum 2017
McGlynn 2003
-
- McGlynn EA, Asch SM, Adams J, Keesey J, Hicks J, DeCristofaro A, et al. The quality of health care delivered to adults in the United States. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;348(26):2635‐45. - PubMed
McGunkin 2006
-
- McGunkin M, Waterman R, Shubin A. Consumer attitudes about health care‐acquired infections and hand hygiene. American Journal of Medical Quality 2006;21(5):342‐6. - PubMed
Moher 2009
-
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, the PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta‐Analyses: the PRISMA statement. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2009;62(10):1006‐12. - PubMed
Ng 2017
Nilsen 2006
-
- Nilsen ES, Myrhaug HT, Johansen M, Oliver S, Oxman AD. Methods of consumer involvement in developing healthcare policy and research, clinical practice guidelines and patient information material. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004563.pub2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
O'Brien 2007
Oxman 1995
Oxman 2005
-
- Oxman AD, Fretheim A, Flottorp S. The OFF theory of research utilization. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58(2):113‐6. - PubMed
Parreira 2017
Peytremann‐Bridevaux 2015
Plomp 2010
-
- Plomp HN, Ballast N. Trust and vulnerability in doctor–patient relations in occupational health. Occupational Medicine 2010;60(4):261‐9. - PubMed
Poquet 2016
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Richards 2013
-
- Richards T, Montori VM, Godlee F, Lapsley P, Paul D. Let the patient revolution begin. Patients can improve healthcare: it's time to take partnership seriously. BMJ 2013;346:f2614. - PubMed
Robertson 2006
-
- Robertson R, Jochelson K. Interventions that change clinician behaviour: mapping the literature. NICE report, 2006. www.nice.org.uk/Media/Default/About/what‐we‐do/Into‐practice/Support‐for... (accessed prior to 7 December 2016).
Runciman 2012
-
- Runciman WB, Hunt TD, Hannaford NA, Hibbert PD, Westbrook JI, Coiera EW, et al. CareTrack: assessing the appropriateness of health care delivery in Australia. Medical Journal of Australia 2012;197(2):100‐5. - PubMed
Sampson 2008
-
- Sampson M, McGowan J, Lefebvre C, Moher D, Grimshaw J. PRESS: Peer Review of Electronic Search Strategies. Ottawa: Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health, 2008.
Schuster 1998
Schwappach 2010a
-
- Schwappach DLB. Engaging patients as viligilant partners in safety. A systematic review. Medical Care Research and Review 2010;67(2):119‐48. - PubMed
Schwappach 2010b
-
- Schwappach DLB, Hochreutener MA, Wernli M. Oncology nurses' perceptions about involving patients in the prevention of chemotherapy administration errors. Oncology Nursing Forum 2010;37(2):E84‐91. - PubMed
Schwappach 2011
-
- Schwappach DLB, Frank O, Kopperberg J, Müller B, Wasserfallen JB. Patients' and healthcare workers' perceptions of a patient safety advisory. International Journal for Quality in Health Care 2011;23(6):713‐20. - PubMed
Schwappach 2013
-
- Schwappach DLB, Frank O, Davis RE. A vignette study to examine health care professionals' attitudes towards patient involvement in error prevention. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice 2013;19(5):840‐8. - PubMed
Seddon 2001
Skirbekk 2011
-
- Skirbekk H, Middelthon AL, Hjortdahl P, Finset A. Mandates of trust in the doctor‐patient relationship. Qualitative Health Research 2011;21(9):1182‐90. - PubMed
Stacey 2017
-
- Stacey D, Légaré F, Lewis K, Barry MJ, Bennett CL, Eden KB, Holmes‐Rovner M, Llewellyn‐Thomas H, Lyddiatt A, Thomson R, Trevena L. Decision aids for people facing health treatment or screening decisions. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2017, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001431.pub5] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Sugavanam 2013
-
- Sugavanam T, Mead G, Bulley C, Donaghy M, Wijck F. The effects and experiences of goal setting in stroke rehabilitation ‐ a systematic review. Disability Rehabilitation 2013;35(3):177‐90. - PubMed
Tzortziou Brown 2016
Ukoumunne 1999
-
- Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JA, Burney PG. Methods for evaluating area‐wide and organisation‐based interventions in health and health care: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment 1999;3(5):iii‐92. - PubMed
Willems 2005
-
- Willems S, Maesschalck S, Deveugele M, Derese A, Maeseneer J. Socio‐economic status of the patient and doctor‐patient communication:does it make a difference?. Patient Education and Counseling 2005;56(2):139‐46. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

