Aggregation of Vibrio cholerae by Cationic Polymers Enhances Quorum Sensing but Overrides Biofilm Dissipation in Response to Autoinduction
- PMID: 30204411
- PMCID: PMC6257621
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.8b00815
Aggregation of Vibrio cholerae by Cationic Polymers Enhances Quorum Sensing but Overrides Biofilm Dissipation in Response to Autoinduction
Abstract
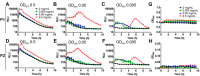
Vibrio cholerae is a Gram-negative bacterium found in aquatic environments and a human pathogen of global significance. Its transition between host-associated and environmental lifestyles involves the tight regulation of niche-specific phenotypes such as motility, biofilm formation, and virulence. V. cholerae's transition from the host to environmental dispersal usually involves suppression of virulence and dispersion of biofilm communities. In contrast to this naturally occurring transition, bacterial aggregation by cationic polymers triggers a unique response, which is to suppress virulence gene expression while also triggering biofilm formation by V. cholerae, an artificial combination of traits that is potentially very useful to bind and neutralize the pathogen from contaminated water. Here, we set out to uncover the mechanistic basis of this polymer-triggered bacterial behavior. We found that bacteria-polymer aggregates undergo rapid autoinduction and achieve quorum sensing at bacterial densities far below those required for autoinduction in the absence of polymers. We demonstrate this induction of quorum sensing is due both to a rapid formation of autoinducer gradients and local enhancement of autoinducer concentrations within bacterial clusters as well as the stimulation of CAI-1 and AI-2 production by aggregated bacteria. We further found that polymers cause an induction of the biofilm-specific regulator VpsR and the biofilm structural protein RbmA, bypassing the usual suppression of biofilm during autoinduction. Overall, this study highlights that synthetic materials can be used to cross-wire natural bacterial responses to achieve a combination of phenotypes with potentially useful applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The intragenus and interspecies quorum-sensing autoinducers exert distinct control over Vibrio cholerae biofilm formation and dispersal.PLoS Biol. 2019 Nov 11;17(11):e3000429. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000429. eCollection 2019 Nov. PLoS Biol. 2019. PMID: 31710602 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum Sensing Autoinducer(s) and Flagellum Independently Mediate EPS Signaling in Vibrio cholerae Through LuxO-Independent Mechanism.Microb Ecol. 2019 Apr;77(3):616-630. doi: 10.1007/s00248-018-1262-5. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Microb Ecol. 2019. PMID: 30218129
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of Indole-Based Autoinducers on Quorum Sensing in Vibrio cholerae.ACS Infect Dis. 2020 Apr 10;6(4):572-576. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.9b00409. Epub 2020 Mar 23. ACS Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32182033
-
Efficient responses to host and bacterial signals during Vibrio cholerae colonization.Gut Microbes. 2014 Jan-Feb;5(1):120-8. doi: 10.4161/gmic.26944. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Gut Microbes. 2014. PMID: 24256715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial gene regulation by alpha-hydroxyketone signaling.Trends Microbiol. 2010 Jul;18(7):288-97. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2010.03.004. Epub 2010 Apr 8. Trends Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20382022 Review.
Cited by
-
Release of extracellular DNA by Pseudomonas sp. as a major determinant for biofilm switching and an early indicator for cell population control.iScience. 2025 Feb 18;28(3):112063. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112063. eCollection 2025 Mar 21. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40124492 Free PMC article.
-
Polymer-induced biofilms for enhanced biocatalysis.Mater Horiz. 2022 Oct 3;9(10):2592-2602. doi: 10.1039/d2mh00607c. Mater Horiz. 2022. PMID: 35912866 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-programmed responsive microorganism assembly with controlled patterns and behaviors.Sci Adv. 2025 Jun 13;11(24):eads8651. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ads8651. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40512851 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum sensing controls Vibrio cholerae multicellular aggregate formation.Elife. 2018 Dec 24;7:e42057. doi: 10.7554/eLife.42057. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30582742 Free PMC article.
-
Vibrio cholerae's mysterious Seventh Pandemic island (VSP-II) encodes novel Zur-regulated zinc starvation genes involved in chemotaxis and cell congregation.PLoS Genet. 2021 Jun 21;17(6):e1009624. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009624. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34153031 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/M01116X/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/M021513/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 177ISSFPP/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AI132354/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- BB/L007916/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

