Expansion of the genetic code via expansion of the genetic alphabet
- PMID: 30205312
- PMCID: PMC6361380
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.08.009
Expansion of the genetic code via expansion of the genetic alphabet
Abstract
Current methods to expand the genetic code enable site-specific incorporation of non-canonical amino acids (ncAAs) into proteins in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. However, current methods are limited by the number of codons possible, their orthogonality, and possibly their effects on protein synthesis and folding. An alternative approach relies on unnatural base pairs to create a virtually unlimited number of genuinely new codons that are efficiently translated and highly orthogonal because they direct ncAA incorporation using forces other than the complementary hydrogen bonds employed by their natural counterparts. This review outlines progress and achievements made towards developing a functional unnatural base pair and its use to generate semi-synthetic organisms with an expanded genetic alphabet that serves as the basis of an expanded genetic code.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
Patent applications have been filed by Synthorx and The Scripps Research Institute covering the UBPs and their use to produce proteins containing ncAAs. F.E.R. also has shares in Synthorx, Inc., a company that has commercial interests in the UBP.
Figures

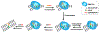
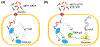
References
-
- Leader B, Baca QJ, Golan DE: Protein therapeutics: a summary and pharmacological classification. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2008, 7:21–39. - PubMed
-
- Chin JW: Expanding and reprogramming the genetic code. Nature 2017, 550:53–60. - PubMed
-
This review provides a recent summary of the amber suppression methodology for precise ncAA incorporation in order to probe, image, and control protein structure and function.
-
- Young DD, Schultz PG: Playing with the molecules of life. ACS Chem Biol 2018, 13:854–870. - PMC - PubMed
-
This review provides a recent summary of the amber suppression methodology, describing improved orthogonal translational machinery for applying ncAAs as probes and the development of new therapeutics.
-
- Italia JS, Addy PS, Wrobel CJ, Crawford LA, Lajoie MJ, Zheng Y, Chatterjee A: An orthogonalized platform for genetic code expansion in both bacteria and eukaryotes. Nat Chem Biol 2017, 13:446–450. - PubMed
-
- Neumann H, Wang K, Davis L, Garcia-Alai M, Chin JW: Encoding multiple unnatural amino acids via evolution of a quadruplet-decoding ribosome. Nature 2010, 464:441–444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

