Salvage Concurrent Chemo-radiation Therapy for Loco-regional Recurrence Following Curative Surgery of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 30205417
- PMCID: PMC6473287
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2018.366
Salvage Concurrent Chemo-radiation Therapy for Loco-regional Recurrence Following Curative Surgery of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: This study is to report clinical outcomes of salvage concurrent chemo-radiation therapy (CCRT) in treating patients with loco-regional recurrence (LRR) following initial complete resection of non-small cell lung cancer.
Materials and methods: Between February 2004 and December 2016, 127 patients underwent salvage CCRT for LRR. The median radiation therapy (RT) dose was 66 Gy and clinical target volume was to cover recurrent lesion with margin without elective inclusion of regional lymphatics. Majority of patients (94.5%) received weekly platinum-based doublet chemotherapy during RT course.
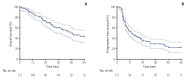
Results: The median follow-up time from the start of CCRT was 25 months. The median survival duration was 49 months, and overall survival (OS) rates at 2 and 5 years were 72.9% and 43.9%. The 2- and 5-year rates of in-field failure-free survival, distant metastasis free survival, and progression free survival were 82.4% and 73.8%, 50.4% and 39.9%, and 34.6% and 22.3%, respectively. Grade ≥ 3 radiation-related esophagitis and pneumonitis occurred in 14 (11.0%) and six patients (4.7%), respectively. On both univariate and multivariate analysis, higher biologically equivalent dose (BED10) (≥ 79.2 Gy10 vs. < 79.2 Gy10; hazard ratio [HR], 0.431), smaller CTV (≤ 80 cm3 vs. > 80 cm3; HR, 0.403), and longer disease-free interval (> 1 year vs. ≤ 1 year; HR, 0.489) were significantly favorable factors for OS.
Conclusion: The current study has demonstrated that high dose salvage CCRT focused to the involved lesion only was highly effective and safe. In particular, higher BED10, smaller CTV, and longer disease-free interval were favorable factors for improved survival.
Keywords: Loco-regional recurrence; Non-small cell lung carcinoma; Salvage concurrent chemo-radiation therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest relevant to this article was not reported.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–86. - PubMed
-
- al-Kattan K, Sepsas E, Fountain SW, Townsend ER. Disease recurrence after resection for stage I lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1997;12:380–4. - PubMed
-
- Williams BA, Sugimura H, Endo C, Nichols FC, Cassivi SD, Allen MS, et al. Predicting postrecurrence survival among completely resected nonsmall-cell lung cancer patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;81:1021–7. - PubMed
-
- Sugimura H, Nichols FC, Yang P, Allen MS, Cassivi SD, Deschamps C, et al. Survival after recurrent nonsmall-cell lung cancer after complete pulmonary resection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;83:409–17. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical