Novel Group of AChE Reactivators-Synthesis, In Vitro Reactivation and Molecular Docking Study
- PMID: 30205495
- PMCID: PMC6225275
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23092291
Novel Group of AChE Reactivators-Synthesis, In Vitro Reactivation and Molecular Docking Study
Abstract
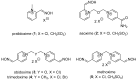
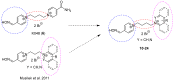
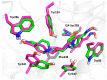
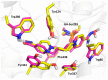
The acetylcholinesterase (AChE) reactivators (e.g., obidoxime, asoxime) became an essential part of organophosphorus (OP) poisoning treatment, together with atropine and diazepam. They are referred to as a causal treatment of OP poisoning, because they are able to split the OP moiety from AChE active site and thus renew its function. In this approach, fifteen novel AChE reactivators were determined. Their molecular design originated from former K-oxime compounds K048 and K074 with remaining oxime part of the molecule and modified part with heteroarenium moiety. The novel compounds were prepared, evaluated in vitro on human AChE (HssAChE) inhibited by tabun, paraoxon, methylparaoxon or DFP and compared to commercial HssAChE reactivators (pralidoxime, methoxime, trimedoxime, obidoxime, asoxime) or previously prepared compounds (K048, K074, K075, K203). Some of presented oxime reactivators showed promising ability to reactivate HssAChE comparable or higher than the used standards. The molecular modelling study was performed with one compound that presented the ability to reactivate GA-inhibited HssAChE. The SAR features concerning the heteroarenium part of the reactivator's molecule are described.
Keywords: acetylcholinesterase; in vitro; molecular docking; organophosphate; oxime; reactivation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
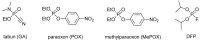


References
-
- Bajgar J. Organophosphates/nerve agent poisoning: Mechanism of action, diagnosis, prophylaxis, and teratment. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2004;38:151–193. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

