Clinical and Biological Characterization of Skin Pigmentation Diversity and Its Consequences on UV Impact
- PMID: 30205563
- PMCID: PMC6163216
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092668
Clinical and Biological Characterization of Skin Pigmentation Diversity and Its Consequences on UV Impact
Abstract
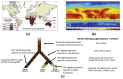
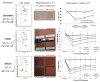
Skin color diversity is the most variable and noticeable phenotypic trait in humans resulting from constitutive pigmentation variability. This paper will review the characterization of skin pigmentation diversity with a focus on the most recent data on the genetic basis of skin pigmentation, and the various methodologies for skin color assessment. Then, melanocyte activity and amount, type and distribution of melanins, which are the main drivers for skin pigmentation, are described. Paracrine regulators of melanocyte microenvironment are also discussed. Skin response to sun exposure is also highly dependent on color diversity. Thus, sensitivity to solar wavelengths is examined in terms of acute effects such as sunburn/erythema or induced-pigmentation but also long-term consequences such as skin cancers, photoageing and pigmentary disorders. More pronounced sun-sensitivity in lighter or darker skin types depending on the detrimental effects and involved wavelengths is reviewed.
Keywords: UV sensitivity; constitutive skin pigmentation; melanocyte; phototype; pigmentary disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare a conflict of interest: all authors are full employees of a cosmetic industry.
Figures




References
-
- Alaluf S., Heath A., Carter N., Atkins D., Mahalingam H., Barrett K., Kolb R., Smit N. Variation in melanin content and composition in type V and VI photoexposed and photoprotected human skin: The dominant role of DHI. Pigment Cell Res. 2001;14:337–347. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0749.2001.140505.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

