MAPINS, a Highly Efficient Detection Method That Identifies Insertional Mutations and Complex DNA Rearrangements
- PMID: 30206105
- PMCID: PMC6288735
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.18.00474
MAPINS, a Highly Efficient Detection Method That Identifies Insertional Mutations and Complex DNA Rearrangements
Abstract
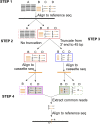
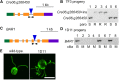
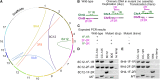
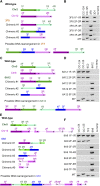
Insertional mutagenesis, in which a piece of exogenous DNA is integrated randomly into the genomic DNA of the recipient cell, is a useful method to generate new mutants with phenotypes of interest. The unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is an outstanding model for studying many biological processes. We developed a new computational algorithm, MAPINS (mapping insertions), to efficiently identify insertion sites created by the integration of an APHVIII (aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase VIII) cassette that confers paromomycin resistance. Using whole-genome sequencing data, this method eliminates the need for genomic DNA manipulation and retains all the sequencing information provided by paired-end sequencing. We experimentally verified 38 insertion sites out of 41 sites (93%) identified by MAPINS from 20 paromomycin-resistant strains. Using meiotic analysis of 18 of these strains, we identified insertion sites that completely cosegregate with paromomycin resistance. In six of the seven strains with a mutant phenotype, we demonstrated complete cosegregation of the mutant phenotype and the verified insertion site. In addition, we provide direct evidence of complex rearrangements of genomic DNA in five strains, three of which involve the APHVIII insertion site. We suggest that strains obtained by insertional mutagenesis are more complicated than expected from previous analyses in Chlamydomonas To map the locations of some complex insertions, we designed 49 molecular markers based on differences identified via whole-genome sequencing between wild-type strains CC-124 and CC-125. Overall, MAPINS provides a low-cost, efficient method to characterize insertional mutants in Chlamydomonas.
© 2018 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Gene. 2001 Oct 17;277(1-2):221-9. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(01)00616-3. Gene. 2001. PMID: 11602359
-
Promoter trapping in microalgae using the antibiotic paromomycin as selective agent.Mar Drugs. 2012 Dec 4;10(12):2749-65. doi: 10.3390/md10122749. Mar Drugs. 2012. PMID: 23211713 Free PMC article.
-
Stable nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a Streptomyces rimosus gene as the selective marker.Gene. 1996 Nov 28;181(1-2):13-8. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(96)00384-8. Gene. 1996. PMID: 8973302
-
Insertional mutagenesis as a tool to study genes/functions in Chlamydomonas.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;616:77-89. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-75532-8_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 18161492 Review.
-
Respiratory-deficient mutants of the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas: a review.Biochimie. 2014 May;100:207-18. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.10.006. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Biochimie. 2014. PMID: 24139906 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative genomics of Chlamydomonas.Plant Cell. 2021 May 31;33(4):1016-1041. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koab026. Plant Cell. 2021. PMID: 33793842 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Delivery Technologies with Applications in Microalgal Genetic Engineering.Biology (Basel). 2021 Mar 26;10(4):265. doi: 10.3390/biology10040265. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33810286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of photosynthesis genes through whole-genome sequencing of acetate-requiring mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.PLoS Genet. 2021 Sep 7;17(9):e1009725. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009725. eCollection 2021 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34492001 Free PMC article.
-
Gene dosage of independent dynein arm motor preassembly factors influences cilia assembly in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.PLoS Genet. 2024 Mar 18;20(3):e1011038. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011038. eCollection 2024 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 38498551 Free PMC article.
-
TIM, a targeted insertional mutagenesis method utilizing CRISPR/Cas9 in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.PLoS One. 2020 May 13;15(5):e0232594. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232594. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32401787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al. (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

