Structural Analysis of the Interaction between the Bacterial Cell Division Proteins FtsQ and FtsB
- PMID: 30206170
- PMCID: PMC6134095
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.01346-18
Structural Analysis of the Interaction between the Bacterial Cell Division Proteins FtsQ and FtsB
Abstract
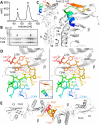
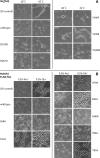
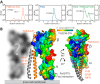
Most bacteria and archaea use the tubulin homologue FtsZ as its central organizer of cell division. In Gram-negative Escherichia coli bacteria, FtsZ recruits cytosolic, transmembrane, periplasmic, and outer membrane proteins, assembling the divisome that facilitates bacterial cell division. One such divisome component, FtsQ, a bitopic membrane protein with a globular domain in the periplasm, has been shown to interact with many other divisome proteins. Despite its otherwise unknown function, it has been shown to be a major divisome interaction hub. Here, we investigated the interactions of FtsQ with FtsB and FtsL, two small bitopic membrane proteins that act immediately downstream of FtsQ. We show in biochemical assays that the periplasmic domains of E. coli FtsB and FtsL interact with FtsQ, but not with each other. Our crystal structure of FtsB bound to the β domain of FtsQ shows that only residues 64 to 87 of FtsB interact with FtsQ. A synthetic peptide comprising those 24 FtsB residues recapitulates the FtsQ-FtsB interactions. Protein deletions and structure-guided mutant analyses validate the structure. Furthermore, the same structure-guided mutants show cell division defects in vivo that are consistent with our structure of the FtsQ-FtsB complex that shows their interactions as they occur during cell division. Our work provides intricate details of the interactions within the divisome and also provides a tantalizing view of a highly conserved protein interaction in the periplasm of bacteria that is an excellent target for cell division inhibitor searches.IMPORTANCE In most bacteria and archaea, filaments of FtsZ protein organize cell division. FtsZ forms a ring structure at the division site and starts the recruitment of 10 to 20 downstream proteins that together form a multiprotein complex termed the divisome. The divisome is thought to facilitate many of the steps required to make two cells out of one. FtsQ and FtsB are part of the divisome, with FtsQ being a central hub, interacting with most of the other divisome components. Here we show for the first time in detail how FtsQ interacts with its downstream partner FtsB and show that mutations that disturb the interface between the two proteins effectively inhibit cell division.
Keywords: FtsL; FtsN; X-ray crystallography; bacterial cell division; biochemistry; divisome; molecular microbiology; periplasm; protein structure-function.
Copyright © 2018 Kureisaite-Ciziene et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Divisome under construction: distinct domains of the small membrane protein FtsB are necessary for interaction with multiple cell division proteins.J Bacteriol. 2009 Apr;191(8):2815-25. doi: 10.1128/JB.01597-08. Epub 2009 Feb 20. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19233928 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-mapping the contact sites of the Escherichia coli cell division proteins FtsB and FtsL on the FtsQ protein.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 23;288(34):24340-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.485888. Epub 2013 Jul 11. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23846696 Free PMC article.
-
A model for the Escherichia coli FtsB/FtsL/FtsQ cell division complex.BMC Struct Biol. 2011 Jun 14;11:28. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-11-28. BMC Struct Biol. 2011. PMID: 21672257 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the assembly and regulation of the bacterial divisome.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2024 Jan;22(1):33-45. doi: 10.1038/s41579-023-00942-x. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 37524757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The divergent early divisome: is there a functional core?Trends Microbiol. 2024 Mar;32(3):231-240. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2023.08.010. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Trends Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 37741788 Review.
Cited by
-
Interrogating the Essential Bacterial Cell Division Protein FtsQ with Fragments Using Target Immobilized NMR Screening (TINS).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 27;20(15):3684. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153684. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31357624 Free PMC article.
-
LC_Glucose-Inhibited Division Protein Is Required for Motility, Biofilm Formation, and Stress Response in Lysobacter capsici X2-3.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 17;13:840792. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.840792. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35369450 Free PMC article.
-
The Staphylococcus aureus cell division protein, DivIC, interacts with the cell wall and controls its biosynthesis.Commun Biol. 2022 Nov 11;5(1):1228. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-04161-7. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36369270 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational changes in the essential E. coli septal cell wall synthesis complex suggest an activation mechanism.Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 31;14(1):4585. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39921-4. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37524712 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in mice requires PerM for successful cell division.Elife. 2019 Nov 21;8:e49570. doi: 10.7554/eLife.49570. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31751212 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
