Multiple Mechanisms Inactivate the LIN-41 RNA-Binding Protein To Ensure a Robust Oocyte-to-Embryo Transition in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 30206186
- PMCID: PMC6218228
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.118.301421
Multiple Mechanisms Inactivate the LIN-41 RNA-Binding Protein To Ensure a Robust Oocyte-to-Embryo Transition in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
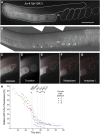
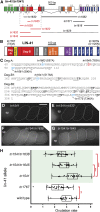
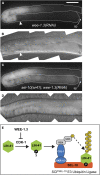
In the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, the conserved LIN-41 RNA-binding protein is a translational repressor that coordinately controls oocyte growth and meiotic maturation. LIN-41 exerts these effects, at least in part, by preventing the premature activation of the cyclin-dependent kinase CDK-1 Here we investigate the mechanism by which LIN-41 is rapidly eliminated upon the onset of meiotic maturation. Elimination of LIN-41 requires the activities of CDK-1 and multiple SCF (Skp1, Cul1, and F-box protein)-type E3 ubiquitin ligase subunits, including the conserved substrate adaptor protein SEL-10/Fbw7/Cdc4, suggesting that LIN-41 is a target of ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation. Within the LIN-41 protein, two nonoverlapping regions, Deg-A and Deg-B, are individually necessary for LIN-41 degradation; both contain several potential phosphodegron sequences, and at least one of these sequences is required for LIN-41 degradation. Finally, Deg-A and Deg-B are sufficient, in combination, to mediate SEL-10-dependent degradation when transplanted into a different oocyte protein. Although LIN-41 is a potent inhibitor of protein translation and M phase entry, the failure to eliminate LIN-41 from early embryos does not result in the continued translational repression of LIN-41 oocyte messenger RNA targets. Based on these observations, we propose a model for the elimination of LIN-41 by the SEL-10 E3 ubiquitin ligase and suggest that LIN-41 is inactivated before it is degraded. Furthermore, we provide evidence that another RNA-binding protein, the GLD-1 tumor suppressor, is regulated similarly. Redundant mechanisms to extinguish translational repression by RNA-binding proteins may both control and provide robustness to irreversible developmental transitions, including meiotic maturation and the oocyte-to-embryo transition.
Keywords: RNA-binding proteins; oocyte meiotic maturation; oocyte-to-embryo transition; translational regulation; ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation.
Copyright © 2018 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ubiquitin ligases and a processive proteasome facilitate protein clearance during the oocyte-to-embryo transition in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2022 May 5;221(1):iyac051. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac051. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 35377419 Free PMC article.
-
LIN-41 and OMA Ribonucleoprotein Complexes Mediate a Translational Repression-to-Activation Switch Controlling Oocyte Meiotic Maturation and the Oocyte-to-Embryo Transition in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2017 Aug;206(4):2007-2039. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.203174. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28576864 Free PMC article.
-
The TRIM-NHL protein LIN-41 and the OMA RNA-binding proteins antagonistically control the prophase-to-metaphase transition and growth of Caenorhabditis elegans oocytes.Genetics. 2014 Dec;198(4):1535-58. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.168831. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 25261698 Free PMC article.
-
The oocyte-to-embryo transition.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;757:351-72. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4015-4_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 22872483 Review.
-
Control of oocyte growth and meiotic maturation in Caenorhabditis elegans.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;757:277-320. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4015-4_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 22872481 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Post-transcriptional repression of CFP-1 expands the regulatory repertoire of LIN-41/TRIM71.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Oct 27;51(19):10668-10680. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad729. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37670562 Free PMC article.
-
Biology of the Caenorhabditis elegans Germline Stem Cell System.Genetics. 2019 Dec;213(4):1145-1188. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.300238. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31796552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of RNA-binding proteins in orchestrating germline development in Caenorhabditis elegans.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jan 4;10:1094295. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1094295. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36684428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Highs and Lows of FBXW7: New Insights into Substrate Affinity in Disease and Development.Cells. 2023 Aug 24;12(17):2141. doi: 10.3390/cells12172141. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37681873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin ligases and a processive proteasome facilitate protein clearance during the oocyte-to-embryo transition in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2022 May 5;221(1):iyac051. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac051. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 35377419 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

