Chronic myeloid leukaemia cells require the bone morphogenic protein pathway for cell cycle progression and self-renewal
- PMID: 30206237
- PMCID: PMC6134087
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-018-0905-2
Chronic myeloid leukaemia cells require the bone morphogenic protein pathway for cell cycle progression and self-renewal
Abstract
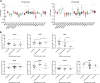
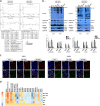
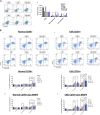
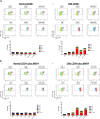
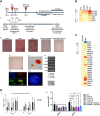
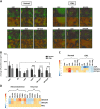
Leukaemic stem cell (LSC) persistence remains a major obstacle to curing chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML). The bone morphogenic protein (BMP) pathway is deregulated in CML, with altered expression and response to the BMP ligands shown to impact on LSC expansion and behaviour. In this study, we determined whether alterations in the BMP pathway gene signature had any predictive value for therapeutic response by profiling 60 CML samples at diagnosis from the UK SPIRIT2 trial and correlating the data to treatment response using the 18-month follow-up data. There was significant deregulation of several genes involved in the BMP pathway with ACV1C, INHBA, SMAD7, SNAIL1 and SMURF2 showing differential expression in relation to response. Therapeutic targeting of CML cells using BMP receptor inhibitors, in combination with tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), indicate a synergistic mode of action. Furthermore, dual treatment resulted in altered cell cycle gene transcription and irreversible cell cycle arrest, along with increased apoptosis compared to single agents. Targeting CML CD34+ cells with BMP receptor inhibitors resulted in fewer cell divisions, reduced numbers of CD34+ cells and colony formation when compared to normal donor CD34+ cells, both in the presence and absence of BMP4. In an induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) model generated from CD34+ hematopoietic cells, we demonstrate altered cell cycle profiles and dynamics of ALK expression in CML-iPSCs in the presence and absence of BMP4 stimulation, when compared to normal iPSC. Moreover, dual targeting with TKI and BMP inhibitor prevented the self-renewal of CML-iPSC and increased meso-endodermal differentiation. These findings indicate that transformed stem cells may be more reliant on BMP signalling than normal stem cells. These changes offer a therapeutic window in CML, with intervention using BMP inhibitors in combination with TKI having the potential to target LSC self-renewal and improve long-term outcome for patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Overcoming BCR::ABL1 dependent and independent survival mechanisms in chronic myeloid leukaemia using a multi-kinase targeting approach.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Nov 29;21(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01363-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 38031192 Free PMC article.
-
A novel HDAC inhibitor chidamide combined with imatinib synergistically targets tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Sep;129:110390. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110390. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32563150
-
Immature CML cells implement a BMP autocrine loop to escape TKI treatment.Blood. 2017 Dec 28;130(26):2860-2871. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-08-801019. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Blood. 2017. PMID: 29138221
-
Targeting BMP signaling in the bone marrow microenvironment of myeloid leukemia.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Apr 29;48(2):411-418. doi: 10.1042/BST20190223. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 32167132 Review.
-
Targeting survival pathways in chronic myeloid leukaemia stem cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;169(8):1693-707. doi: 10.1111/bph.12183. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23517124 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overcoming BCR::ABL1 dependent and independent survival mechanisms in chronic myeloid leukaemia using a multi-kinase targeting approach.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Nov 29;21(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01363-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 38031192 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Cells Impair Dendritic Cell and Macrophage Differentiation: Role of BMP4.Cells. 2019 Jul 14;8(7):722. doi: 10.3390/cells8070722. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31337120 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells: targeting therapeutic implications.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Dec 18;12(1):603. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02659-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34922630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of contextual signal TGF-β1 inducer of epithelial mesenchymal transition in metastatic lung adenocarcinoma patients with brain metastases: an update on its pathological significance and therapeutic potential.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2019;23(4):187-194. doi: 10.5114/wo.2019.91543. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2019. PMID: 31992949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered BMP2/4 Signaling in Stem Cells and Their Niche: Different Cancers but Similar Mechanisms, the Example of Myeloid Leukemia and Breast Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 3;9:787989. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.787989. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35047500 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Holyoake T, Jiang X, Eaves C, Eaves A. Isolation of a highly quiescent subpopulation of primitive leukemic cells in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1999;94:2056–2064. - PubMed
-
- Jamieson, C. H. Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program2008, 436–442 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

