Reconfiguration of the plastid genome in Lamprocapnos spectabilis: IR boundary shifting, inversion, and intraspecific variation
- PMID: 30206286
- PMCID: PMC6134119
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-31938-w
Reconfiguration of the plastid genome in Lamprocapnos spectabilis: IR boundary shifting, inversion, and intraspecific variation
Abstract
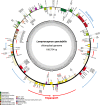
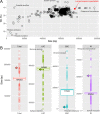
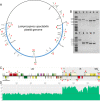
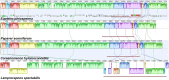
We generated a complete plastid genome (plastome) sequence for Lamprocapnos spectabilis, providing the first complete plastome from the subfamily Fumarioideae (Papaveraceae). The Lamprocapnos plastome shows large differences in size, structure, gene content, and substitution rates compared with two sequenced Papaveraceae plastomes. We propose a model that explains the major rearrangements observed, involving at least six inverted repeat (IR) boundary shifts and five inversions, generating a number of gene duplications and relocations, as well as a two-fold expansion of the IR and miniaturized small single-copy region. A reduction in the substitution rates for genes transferred from the single-copy regions to the IR was observed. Accelerated substitution rates of plastid accD and clpP were detected in the Lamprocapnos plastome. The accelerated substitution rate for the accD gene was correlated with a large insertion of amino acid repeat (AAR) motifs in the middle region, but the forces driving the higher substitution rate of the clpP gene are unclear. We found a variable number of AARs in Lamprocapnos accD and ycf1 genes within individuals, and the repeats were associated with coiled-coil regions. In addition, comparative analysis of three Papaveraceae plastomes revealed loss of rps15 in Papaver, and functional replacement to the nucleus was identified.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ruhlman, T. A. & Jansen, R. K. In Chloroplast Biotechnology: Methods and Protocols (ed. Pal Maliga) 3–38 (Humana Press, 2014).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

