A genome-wide search for new imprinted genes in the human placenta identifies DSCAM as the first imprinted gene on chromosome 21
- PMID: 30206355
- PMCID: PMC6303248
- DOI: 10.1038/s41431-018-0267-3
A genome-wide search for new imprinted genes in the human placenta identifies DSCAM as the first imprinted gene on chromosome 21
Abstract
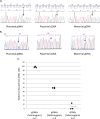
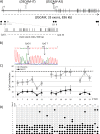
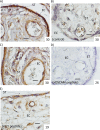
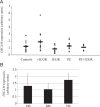
We identified, through a genome-wide search for new imprinted genes in the human placenta, DSCAM (Down Syndrome Cellular Adhesion Molecule) as a paternally expressed imprinted gene. Our work revealed the presence of a Differentially Methylated Region (DMR), located within intron 1 that might regulate the imprinting in the region. This DMR showed a maternal allele methylation, compatible with its paternal expression. We showed that DSCAM is present in endothelial cells and the syncytiotrophoblast layer of the human placenta. In mouse, Dscam expression is biallelic in foetal brain and placenta excluding any possible imprinting in these tissues. This gene encodes a cellular adhesion molecule mainly known for its role in neurone development but its function in the placenta remains unclear. We report here the first imprinted gene located on human chromosome 21 with potential clinical implications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of the mouse paternally expressed imprinted gene Zdbf2 on chromosome 1 and its imprinted human homolog ZDBF2 on chromosome 2.Genomics. 2009 May;93(5):461-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2008.12.012. Epub 2009 Feb 4. Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19200453
-
DNMT1 and AIM1 Imprinting in human placenta revealed through a genome-wide screen for allele-specific DNA methylation.BMC Genomics. 2013 Oct 5;14:685. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-685. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24094292 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphic Imprinting of SLC38A4 Gene in Bovine Placenta.Biochem Genet. 2018 Dec;56(6):639-649. doi: 10.1007/s10528-018-9866-5. Epub 2018 May 21. Biochem Genet. 2018. PMID: 29785670
-
Genomic imprinting in the placenta.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2006;113(1-4):90-8. doi: 10.1159/000090819. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2006. PMID: 16575167 Review.
-
Imprinted genes in the placenta--a review.Placenta. 2005 Apr;26 Suppl A:S10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2004.12.009. Placenta. 2005. PMID: 15837057 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic and epigenetic sex-specific adaptations to endurance exercise.Epigenetics. 2019 Jun;14(6):523-535. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2019.1603961. Epub 2019 Apr 13. Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 30957644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety of embryo cryopreservation: insights from mid-term placental transcriptional changes.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024 Jul 12;22(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12958-024-01241-7. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 38997724 Free PMC article.
-
Imprinting as Basis for Complex Evolutionary Novelties in Eutherians.Biology (Basel). 2024 Aug 31;13(9):682. doi: 10.3390/biology13090682. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Epigenetics in Placental Development and the Etiology of Preeclampsia.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 11;20(11):2837. doi: 10.3390/ijms20112837. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31212604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Placental DNA methylation in pregnancies complicated by maternal diabetes and/or obesity: State of the art and research gaps.Epigenetics. 2022 Dec;17(13):2188-2208. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2022.2111755. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Epigenetics. 2022. PMID: 35950598 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

