First Opioid Prescription and Subsequent High-Risk Opioid Use: a National Study of Privately Insured and Medicare Advantage Adults
- PMID: 30206790
- PMCID: PMC6258623
- DOI: 10.1007/s11606-018-4628-y
First Opioid Prescription and Subsequent High-Risk Opioid Use: a National Study of Privately Insured and Medicare Advantage Adults
Abstract
Background: National guidelines make recommendations regarding the initial opioid prescriptions, but most of the supporting evidence is from the initial episode of care, not the first prescription.
Objective: To examine associations between features of the first opioid prescription and high-risk opioid use in the 18 months following the first prescription.
Design: Retrospective cohort study using data from a large commercial insurance claims database for 2011-2014 to identify individuals with no recent use of opioids and follow them for 18 months after the first opioid prescription.
Participants: Privately insured patients aged 18-64 and Medicare Advantage patients aged 65 or older who filled a first opioid prescription between 07/01/2011 and 06/30/2013.
Main outcomes and measures: High-risk opioid use was measured by having (1) opioid prescriptions overlapping for 7 days or more, (2) opioid and benzodiazepine prescriptions overlapping for 7 days or more, (3) three or more prescribers of opioids, and (4) a daily dosage exceeding 120 morphine milligram equivalents, in each of the six quarters following the first prescription.
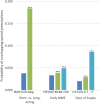
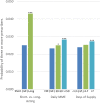
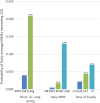
Key results: All three features of the first prescription were strongly associated with high-risk use. For example, among privately insured patients, receiving a long- (vs. short-) acting first opioid was associated with a 16.9-percentage-point increase (95% CI, 14.3-19.5), a daily MME of 50 or more (vs. less than 30) was associated with a 12.5-percentage-point increase (95% CI, 12.1-12.9), and a supply exceeding 7 days (vs. 3 or fewer days) was associated with a 4.8-percentage-point increase (95% CI, 4.5-5.2), in the probability of having a daily dosage of 120 MMEs or more in the long term, compared to a sample mean of 4.2%. Results for the Medicare Advantage patients were similar.
Conclusions: Long-acting formulation, high daily dosage, and longer duration of the first opioid prescription were each associated with increased high-risk use of opioids in the long term.
Keywords: health services research; pain; physician behavior; prescription drug abuse.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have a conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Number and age-adjusted rates of drug-poisoning deaths involving opioid analgesics and heroin: United States, 2000-2014. National Vital Statistics System, Mortality Filehttps://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/health_policy/AADR_drug_poisoning_involvin.... Accessed July 13, 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

