A review of quality of life (QOL) assessments and indicators: Towards a "QOL-Climate" assessment framework
- PMID: 30206898
- PMCID: PMC6486941
- DOI: 10.1007/s13280-018-1090-3
A review of quality of life (QOL) assessments and indicators: Towards a "QOL-Climate" assessment framework
Abstract
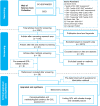
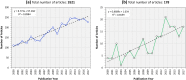
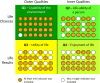
Quality of life (QOL), although a complex and amorphous concept, is a term that warrants attention, especially in discussions on issues that touch on the impacts of climate change and variability. Based on the principles of RepOrting standards for Systematic Evidence Synthesis, we present a systematic review aimed at gaining insights into the conceptualization and methodological construct of previous studies regarding QOL and QOL-related indexes. We find that (i) QOL assessments vary in terms of conceptual foundations, dimensions, indicators, and units of analysis, (ii) social indicators are consistently used across assessments, (iii) most assessments consider indicators that pertain to the livability of the environment, and (iv) QOL can be based on objective indicators and/or subjective well-being, and on a composite index or unaggregated dimensions and indicators. However, we also find that QOL assessments remain poorly connected with climate-related issues, an important research gap. Our proposed "QOL-Climate" assessment framework, designed to capture the social-ecological impacts of climate change and variability, can potentially help fill this gap.
Keywords: Climate change; QOL; Quality of life; Social indicators; Vulnerability; Well-being.
Figures

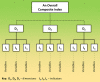
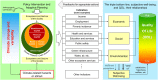
References
-
- Adger WN, Barnett J, Brown K, Marshall N, O’brien K. Cultural dimensions of climate change impacts and adaptation. Nature Climate Change. 2013;3:112–117. doi: 10.1038/nclimate1666. - DOI
-
- Albouy D, Graf W, Kellogg R, Wolff H. Climate amenities, climate change, and american quality of life. Journal of the Association of Environmental and Resource Economists. 2014;3:205–246. doi: 10.1086/684573. - DOI
-
- Atanasova I, Karashtranova E. A novel approach for quality of life evaluation: Rule-based expert system. Social Indicators Research. 2016;128:709–722. doi: 10.1007/s11205-015-1052-0. - DOI
-
- Baptista SR. Design and Use of Composite Indices in Assessment of Climate Change Vulnerability and Resilience. CIESIN: The Earth Institute, Columbia University; 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

