A school- and community-based intervention to promote healthy lifestyle and prevent type 2 diabetes in vulnerable families across Europe: design and implementation of the Feel4Diabetes-study
- PMID: 30207513
- PMCID: PMC10260800
- DOI: 10.1017/S1368980018002136
A school- and community-based intervention to promote healthy lifestyle and prevent type 2 diabetes in vulnerable families across Europe: design and implementation of the Feel4Diabetes-study
Abstract
Objective: To describe the design of the Feel4Diabetes-intervention and the baseline characteristics of the study sample.
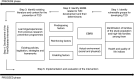
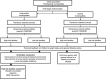
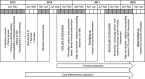
Design: School- and community-based intervention with cluster-randomized design, aiming to promote healthy lifestyle and tackle obesity and obesity-related metabolic risk factors for the prevention of type 2 diabetes among families from vulnerable population groups. The intervention was implemented in 2016-2018 and included: (i) the 'all-families' component, provided to all children and their families via a school- and community-based intervention; and (ii) an additional component, the 'high-risk families' component, provided to high-risk families for diabetes as identified with a discrete manner by the FINDRISC questionnaire, which comprised seven counselling sessions (2016-2017) and a text-messaging intervention (2017-2018) delivered by trained health professionals in out-of-school settings. Although the intervention was adjusted to local needs and contextual circumstances, standardized protocols and procedures were used across all countries for the process, impact, outcome and cost-effectiveness evaluation of the intervention.
Setting: Primary schools and municipalities in six European countries.
Subjects: Families (primary-school children, their parents and grandparents) were recruited from the overall population in low/middle-income countries (Bulgaria, Hungary), from low socio-economic areas in high-income countries (Belgium, Finland) and from countries under austerity measures (Greece, Spain).
Results: The Feel4Diabetes-intervention reached 30 309 families from 236 primary schools. In total, 20 442 families were screened and 12 193 'all families' and 2230 'high-risk families' were measured at baseline.
Conclusions: The Feel4Diabetes-intervention is expected to provide evidence-based results and key learnings that could guide the design and scaling-up of affordable and potentially cost-effective population-based interventions for the prevention of type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Children; Families; Obesity; Type 2 diabetes; Vulnerable.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (2011) Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2010. Geneva: WHO.
-
- International Diabetes Federation (2017) IDF Diabetes Atlas 8th Edition (2017). https://www.idf.org/e-library/epidemiology-research/diabetes-atlas.html (accessed August 2018).
-
- Wandell PE (2005) Quality of life of patients with diabetes mellitus. An overview of research in primary health care in the Nordic countries. Scand J Prim Health Care 23, 68–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

