Correlation between posterior tibial slope and sagittal alignment under weight-bearing conditions in osteoarthritic knees
- PMID: 30208059
- PMCID: PMC6135388
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202488
Correlation between posterior tibial slope and sagittal alignment under weight-bearing conditions in osteoarthritic knees
Abstract
Introduction: Posterior tibial slope (PTS) and sagittal alignment are important factors in the etiology of knee osteoarthritis and knee surgery. Clinically, sagittal alignment, which indicates flexion contracture of the knee, contributes to knee function in weight-bearing (WB) conditions. PTS and sagittal alignment under WB conditions in varus osteoarthritic knees are presumed to affect each other, but their association remains unclear. In this study, we aimed to clarify the association.
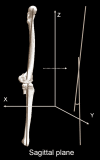
Material and methods: In total, 140 osteoarthritic varus knees were investigated. Under WB conditions, a three-dimensional (3D) alignment assessment system was applied via biplanar long-leg X-rays, using 3D-to-2D image registration technique. The evaluation parameters were as follows: 1) 3D mechanical flexion angle (3DMFA) in regards to sagittal alignment, 2) passing point in the WB line (PP), and 3) medial and lateral PTS.
Results: The medial and lateral PTS showed a positive correlation with 3DMFA and PP, respectively (medial PTS-3DMFA, p = 0.001; medial PTS-PP, p < 0.0001; lateral PTS-3DMFA, p < 0.0001; lateral PTS-PP, p = 0.002). The flexion contracture group with 3DMFA >5° demonstrated greater PTS than non-flexion contracture group (medial PTS, p = 0.006; lateral PTS, p = 0.006).
Conclusions: Both medial and lateral PTS were correlated with sagittal alignment under WB conditions and were larger in the flexion contracture group. This finding can explain the function to take the load articular surface parallel to the ground for holding the balance in WB conditions in the sagittal plane for osteoarthritic knees. Moreover, surgeons may be required to decrease the PTS during knee arthroplasty to restore full extension in knees of patients with fixed flexion contracture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



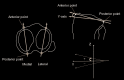
Similar articles
-
Articular surface of the medial proximal tibia is aligned parallel to the ground in three-dimensional space under weight-bearing conditions in healthy and varus osteoarthritic knees.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020 Oct;28(10):3232-3239. doi: 10.1007/s00167-019-05829-0. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020. PMID: 31853619
-
Influence of posterior tibial slope on three-dimensional femorotibial alignment under weight-bearing conditions in healthy Japanese elderly people.Biomed Mater Eng. 2021;32(3):183-194. doi: 10.3233/BME-201209. Biomed Mater Eng. 2021. PMID: 33967036
-
Significant effect of the posterior tibial slope on the weight-bearing, midflexion in vivo kinematics after cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2014 Dec;29(12):2324-30. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2013.10.018. Epub 2013 Oct 24. J Arthroplasty. 2014. PMID: 24269068
-
A comparative study of weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing 3-dimensional lower extremity alignment in knee osteoarthritis.J Orthop Sci. 2020 Sep;25(5):874-879. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2019.11.012. Epub 2020 Jan 16. J Orthop Sci. 2020. PMID: 31955959
-
Osteoarthritic knees have a highly variable patellofemoral alignment: a systematic review.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021 Feb;29(2):483-490. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-05928-3. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021. PMID: 32162047
Cited by
-
Association between three-dimensional gait kinematics and joint-line inclination in osteoarthritic knees compared with normal knees: An epidemiological study.J Exp Orthop. 2024 Jun 11;11(3):e12040. doi: 10.1002/jeo2.12040. eCollection 2024 Jul. J Exp Orthop. 2024. PMID: 38863941 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-articular Injection of Mesenchymal Stem Cells After High Tibial Osteotomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Orthop J Sports Med. 2022 Nov 23;10(11):23259671221133784. doi: 10.1177/23259671221133784. eCollection 2022 Nov. Orthop J Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 36452339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The medial inclination of the proximal tibia is associated with the external knee adduction moment in advanced varus knee osteoarthritis.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022 Feb;30(2):574-583. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-06323-8. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022. PMID: 33067660
-
Effect on inclined medial proximal tibial articulation for varus alignment in advanced knee osteoarthritis.J Exp Orthop. 2019 Mar 28;6(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s40634-019-0180-x. J Exp Orthop. 2019. PMID: 30923977 Free PMC article.
-
Greater medial proximal tibial slope is associated with bone marrow lesions in middle-aged women with early knee osteoarthritis.J Orthop Traumatol. 2023 Nov 28;24(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s10195-023-00739-x. J Orthop Traumatol. 2023. PMID: 38015276 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Whiteside LA, Amador D. The effect of posterior tibial slope on knee stability after Ortholoc total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1988;3:S51–7. - PubMed
-
- Hernigou P, Deschamps G. Posterior slope of the tibial implant and the outcome of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A:506–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

