Spray-dried plasma attenuates inflammation and lethargic behaviors of pregnant mice caused by lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 30208071
- PMCID: PMC6135513
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203427
Spray-dried plasma attenuates inflammation and lethargic behaviors of pregnant mice caused by lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
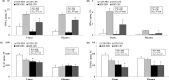
This study evaluated whether dietary spray-dried plasma (SDP) can ameliorate inflammation, lethargic behaviors, and impairment of reproduction caused by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge during late pregnancy. Two experiments were conducted with 125 mated female mice (C57BL/6 strain) in each experiment. All mice were shipped from a vendor on the gestation day (GD) 1 and arrived at the laboratory on GD 3. Mice were randomly assigned to dietary treatments with or without 8% SDP in the diet. On GD 17, mice determined pregnant by BW and abdomen shape were randomly assigned to intraperitoneal injections with or without 2 μg LPS. In experiment 1, 17 mice (26.7 ± 1.7 g BW) were identified pregnant and euthanized 6 h after the LPS challenge to measure inflammatory responses in uterus and placenta. In experiment 2, 44 mice (26.0 ± 1.6 g BW) were identified pregnant and euthanized 24 h after the LPS challenge to assess behavior and late-term pregnancy loss. Growth performance and reproductive responses, such as loss of pregnancy, percentage of fetal death, and etc., were measured in all pregnant mice. The LPS challenge increased (P < 0.05) uterine and placental tumor necrosis factor-α and interferon-γ, late-term pregnancy loss, and lethargy score, and decreased (P < 0.05) uterine transforming growth factor-β1, moving time and number of rearing, and growth and feed intake. The SDP decreased (P < 0.05) concentrations of both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in one or both tissues, and the lethargy score, and increased (P < 0.05) moving time and number of rearing, growth of pregnant mice, and fetal weight. However, the SDP did not affect late-term pregnancy loss caused by the LPS challenge. Consequently, dietary SDP attenuated acute inflammation and lethargic behaviors of pregnant mice caused by the LPS challenge, but did not affect late-term pregnancy loss after the acute inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following interests: Joy M. Campbell, Javier Polo, Joe D. Crenshaw are affiliated with the commercial company, APC Inc., Ankeny, Iowa, United States of America (http://www.functionalproteins.com/). There are no other interests to declare. This does not alter the authors’ adherence to all PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

References
-
- Rivera DL, Olister SM, Liu X, Thompson JH, Zhang XJ, Pennline K, et al. Interleukin-10 attenuates experimental fetal growth restriction and demise. FASEB J. 1998;12: 189–197. - PubMed
-
- Robertson SA, Skinner RJ, Care AS. Essential role of IL-10 in resistance to lipopolysaccharide-induced preterm labor in mice. J. Immunol. 2006;177: 4888–4896. - PubMed
-
- Rubio APD, Correa F, Aisember J, Dorfman D, Bariani MV, Rosenstein RE, et al. Maternal administration of melatonin exerts short- and long-term neuroprotective effects on the offspring from lipopolysaccharide-treated mice. J. Pineal. Res. 2017;63: e12439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

