Supernumerary Incisors in CB6F1 Mice Conditioned with Chemotherapy and Total Body Irradiation before Bone Marrow Transplantation
- PMID: 30208992
- PMCID: PMC6200027
- DOI: 10.30802/AALAS-CM-18-000043
Supernumerary Incisors in CB6F1 Mice Conditioned with Chemotherapy and Total Body Irradiation before Bone Marrow Transplantation
Abstract
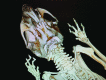
Multiple adult female CB6F1 mice presented with supernumerary incisors after preconditioning with chemotherapy and total body irradiation for bone marrow transplantation (BMT). Mice received nonmyeloablative total body irradiation (3 Gy) and either cyclophosphamide or bendamustine, followed by BMT and posttransplantation cyclophosphamide or bendamustine. Here we describe the clinical presentation, μCT findings, and histopathologic evaluation of the affected mice. These analyses confirmed the gross diagnosis and revealed details of the abnormal tooth morphology. We surmise that the combination of total body irradiation and chemotherapy resulted in the abnormal formation of supernumerary incisors. Supernumerary teeth should be considered as a potential confounding factor in tracking weight loss after BMT. These conditions can be managed to allow animals to reach their intended scientific endpoint.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Total-body irradiation before bone marrow transplantation for acute leukemia in first or second complete remission. Results and prognostic factors in 326 consecutive patients.Strahlenther Onkol. 1998 Feb;174(2):92-104. doi: 10.1007/BF03038482. Strahlenther Onkol. 1998. PMID: 9487372 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Interstitial pneumonitis following autologous bone-marrow transplantation conditioned with cyclophosphamide and total-body irradiation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996 Jan 1;34(1):71-7. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(95)02063-2. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996. PMID: 12118567
-
Efficacy of etoposide, cyclophosphamide, and total body irradiation in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for adult patients with hematological malignancies.Clin Transplant. 2004 Oct;18(5):552-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2004.00225.x. Clin Transplant. 2004. PMID: 15344959
-
Principles of bone marrow transplantation (BMT): providing optimal veterinary and husbandry care to irradiated mice in BMT studies.J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2009 Jan;48(1):11-22. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2009. PMID: 19245745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The early complications of bone marrow transplantation.Semin Hematol. 1984 Apr;21(2):101-8. Semin Hematol. 1984. PMID: 6377500 Review. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

