The kinetoplastid kinetochore protein KKT4 is an unconventional microtubule tip-coupling protein
- PMID: 30209069
- PMCID: PMC6219724
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201711181
The kinetoplastid kinetochore protein KKT4 is an unconventional microtubule tip-coupling protein
Abstract
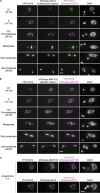
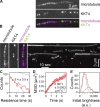
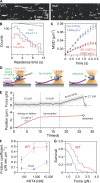
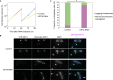
Kinetochores are multiprotein machines that drive chromosome segregation by maintaining persistent, load-bearing linkages between chromosomes and dynamic microtubule tips. Kinetochores in commonly studied eukaryotes bind microtubules through widely conserved components like the Ndc80 complex. However, in evolutionarily divergent kinetoplastid species such as Trypanosoma brucei, which causes sleeping sickness, the kinetochores assemble from a unique set of proteins lacking homology to any known microtubule-binding domains. Here, we show that the T. brucei kinetochore protein KKT4 binds directly to microtubules and maintains load-bearing attachments to both growing and shortening microtubule tips. The protein localizes both to kinetochores and to spindle microtubules in vivo, and its depletion causes defects in chromosome segregation. We define a microtubule-binding domain within KKT4 and identify several charged residues important for its microtubule-binding activity. Thus, despite its lack of significant similarity to other known microtubule-binding proteins, KKT4 has key functions required for driving chromosome segregation. We propose that it represents a primary element of the kinetochore-microtubule interface in kinetoplastids.
© 2018 Llauró et al.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

