Enzymatic synthesis and chemical inversion provide both enantiomers of bioactive epoxydocosapentaenoic acids
- PMID: 30209076
- PMCID: PMC6210906
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.D089136
Enzymatic synthesis and chemical inversion provide both enantiomers of bioactive epoxydocosapentaenoic acids
Abstract
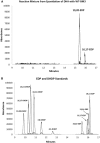
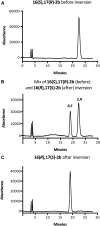
Epoxy PUFAs are endogenous cytochrome P450 (P450) metabolites of dietary PUFAs. Although these metabolites exert numerous biological effects, attempts to study their complex biology have been hampered by difficulty in obtaining the epoxides as pure regioisomers and enantiomers. To remedy this, we synthesized 19,20- and 16,17-epoxydocosapentaenoic acids (EDPs) (the two most abundant EDPs in vivo) by epoxidation of DHA with WT and the mutant (F87V) P450 enzyme BM3 from Bacillus megaterium WT epoxidation yielded a 4:1 mixture of 19,20:16,17-EDP exclusively as (S,R) enantiomers. Epoxidation with the mutant (F87V) yielded a 1.6:1 mixture of 19,20:16,17-EDP; the 19,20-EDP fraction was ∼9:1 (S,R):(R,S), but the 16,17-EDP was exclusively the (S,R) enantiomer. To access the (R,S) enantiomers of these EDPs, we used a short (four-step) chemical inversion sequence, which utilizes 2-(phenylthio)ethanol as the epoxide-opening nucleophile, followed by mesylation of the resulting alcohol, oxidation of the thioether moiety, and base-catalyzed elimination. This short synthesis cleanly converts the (S,R)-epoxide to the (R,S)-epoxide without loss of enantiopurity. This method, also applicable to eicosapentaenoic acid and arachidonic acid, provides a simple, cost-effective procedure for accessing larger amounts of these metabolites.
Keywords: chemoenzymatic synthesis; cytochrome P450; docosahexaenoic acid; epoxide inversion; epoxy fatty acids; lipids/chemistry; polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Copyright © 2018 Cinelli et al.
Figures


References
-
- Campbell W. B., Gebremedhin D., Pratt P. F., and Harder D. R.. 1996. Identification of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids as endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factors. Circ. Res. 78: 415–423. - PubMed
-
- Ye D., Zhang D., Oltman C., Dellsperger K., Lee H. C., and VanRollins M.. 2002. Cytochrome p-450 epoxygenase metabolites of docosahexaenoate potently dilate coronary arterioles by activating large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 303: 768–776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

