LRRK2 and its substrate Rab GTPases are sequentially targeted onto stressed lysosomes and maintain their homeostasis
- PMID: 30209220
- PMCID: PMC6166828
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1812196115
LRRK2 and its substrate Rab GTPases are sequentially targeted onto stressed lysosomes and maintain their homeostasis
Abstract
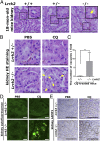
Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) has been associated with a variety of human diseases, including Parkinson's disease and Crohn's disease, whereas LRRK2 deficiency leads to accumulation of abnormal lysosomes in aged animals. However, the cellular roles and mechanisms of LRRK2-mediated lysosomal regulation have remained elusive. Here, we reveal a mechanism of stress-induced lysosomal response by LRRK2 and its target Rab GTPases. Lysosomal overload stress induced the recruitment of endogenous LRRK2 onto lysosomal membranes and activated LRRK2. An upstream adaptor Rab7L1 (Rab29) promoted the lysosomal recruitment of LRRK2. Subsequent family-wide screening of Rab GTPases that may act downstream of LRRK2 translocation revealed that Rab8a and Rab10 were specifically accumulated on overloaded lysosomes dependent on their phosphorylation by LRRK2. Rab7L1-mediated lysosomal targeting of LRRK2 attenuated the stress-induced lysosomal enlargement and promoted lysosomal secretion, whereas Rab8 stabilized by LRRK2 on stressed lysosomes suppressed lysosomal enlargement and Rab10 promoted lysosomal secretion, respectively. These effects were mediated by the recruitment of Rab8/10 effectors EHBP1 and EHBP1L1. LRRK2 deficiency augmented the chloroquine-induced lysosomal vacuolation of renal tubules in vivo. These results implicate the stress-responsive machinery composed of Rab7L1, LRRK2, phosphorylated Rab8/10, and their downstream effectors in the maintenance of lysosomal homeostasis.
Keywords: LRRK2; Rab GTPase; lysosome; phosphorylation.
Copyright © 2018 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of Rab29 at Ser185 regulates its localization and role in the lysosomal stress response in concert with LRRK2.J Cell Sci. 2023 Jul 15;136(14):jcs261003. doi: 10.1242/jcs.261003. Epub 2023 Jul 21. J Cell Sci. 2023. PMID: 37365944 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of lysosomotropic agents on LRRK2 activation and Rab10 phosphorylation.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Nov;145:105081. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.105081. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32919031
-
LRRK2 phosphorylates membrane-bound Rabs and is activated by GTP-bound Rab7L1 to promote recruitment to the trans-Golgi network.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 Jan 15;27(2):385-395. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx410. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 29177506 Free PMC article.
-
LRRK2 and Rab GTPases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2018 Dec 17;46(6):1707-1712. doi: 10.1042/BST20180470. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018. PMID: 30467121 Review.
-
Cellular functions of LRRK2 implicate vesicular trafficking pathways in Parkinson's disease.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Dec 15;44(6):1603-1610. doi: 10.1042/BST20160228. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 27913668 Review.
Cited by
-
Lysosomal positioning regulates Rab10 phosphorylation at LRRK2+ lysosomes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Oct 25;119(43):e2205492119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2205492119. Epub 2022 Oct 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36256825 Free PMC article.
-
Is Glial Dysfunction the Key Pathogenesis of LRRK2-Linked Parkinson's Disease?Biomolecules. 2023 Jan 15;13(1):178. doi: 10.3390/biom13010178. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36671564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Developments in LRRK2-Targeted Therapy for Parkinson's Disease.Drugs. 2019 Jul;79(10):1037-1051. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-01139-4. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31161537 Review.
-
Inhibitory role of peroxiredoxin 2 in LRRK2 kinase activity induced cellular pathogenesis.J Biomed Res. 2019 Jul 31;34(2):103-113. doi: 10.7555/JBR.33.20190090. J Biomed Res. 2019. PMID: 32305964 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of Rab29 at Ser185 regulates its localization and role in the lysosomal stress response in concert with LRRK2.J Cell Sci. 2023 Jul 15;136(14):jcs261003. doi: 10.1242/jcs.261003. Epub 2023 Jul 21. J Cell Sci. 2023. PMID: 37365944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paisán-Ruíz C, et al. Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson’s disease. Neuron. 2004;44:595–600. - PubMed
-
- Zimprich A, et al. Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron. 2004;44:601–607. - PubMed
-
- Lill CM, et al. 23andMe Genetic Epidemiology of Parkinson’s Disease Consortium; International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics Consortium; Parkinson’s Disease GWAS Consortium; Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2) Comprehensive research synopsis and systematic meta-analyses in Parkinson’s disease genetics: The PDGene database. PLoS Genet. 2012;8:e1002548. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang FR, et al. Genomewide association study of leprosy. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:2609–2618. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

