Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing the Effects of Vonoprazan Plus Rebamipide and Esomeprazole Plus Rebamipide on Gastric Ulcer Healing Induced by Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- PMID: 30210115
- PMCID: PMC6378166
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1146-18
Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing the Effects of Vonoprazan Plus Rebamipide and Esomeprazole Plus Rebamipide on Gastric Ulcer Healing Induced by Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Abstract
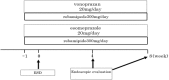
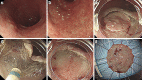
Objective Gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is currently a standard procedure, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are most commonly used to treat post-ESD ulcers. Vonoprazan, a potassium-competitive acid blocker (P-CAB), reportedly inhibits gastric acid secretions more effectively than PPIs. Combination therapy of a PPI plus rebamipide is effective for treating larger ulcers. Our goal was to evaluate the effects of vonoprazan plus rebamipide compared to esomeprazole plus rebamipide for the treatment of post-ESD ulcers. Methods First, vonoprazan plus rebamipide (V group) or esomeprazole plus rebamipide (E group) was orally administered to subjects for eight weeks. We then evaluated the ulcer healing process at four and eight weeks after the procedure using a gastric ulcer stage system and by measuring the ulcer size. Patients A total of 84 patients who underwent ESD for gastric neoplasms between September 2015 and December 2017 in Tsuchiura Kyodo General Hospital were included in this randomized controlled trial. Results The ulcer scar rates at week 4 in the V group (n=43) and E groups (n=39) were 20.9% and 15.4%, while those at week 8 were 90.7% and 92.3%, respectively. The ulcer reduction rates at week 4 in the V and E groups were 94.6% and 93.8%, and those at week 8 were 99.7% and 99.3%, respectively. The ulcer scar rates and reduction rates were not significantly different between the two groups. Conclusion Combination therapy consisting of vonoprazan plus rebamipide was not superior to that of esomeprazole plus rebamipide for post-ESD ulcer healing (UMIN000019516).
Keywords: artificial ulcer; endoscopic submucosal dissection; esomeprazole; gastric intraepithelial neoplasm; ulcer healing; vonoprazan.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Kakushima N, Yahagi N, Fujishiro M, et al. . The healing process of gastric artificial ulcers after endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Endosc 16: 327-331, 2004.
-
- Kakushima N, Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, et al. . Helicobactor pylori status and the extent of gastric atorotphy do not affect ulcer healing after endoscopic submucosal dissection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 21: 1586-1589, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Oh TH, Jung HY, Choi KD, et al. . Degree of healing and healing-associated factors of endoscopic submucosal dissection-induced ulcers after pantoprazole therapy for four weeks. Dig Dis Sci 54: 1494-1499, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Kato T, Araki H, Onogi F, et al. . Clinical trial: rebamipide promotes gastric ulcer healing by proton pump inhibitor after endoscopic submucosal dissection-a randomized controlled study. J Gastroenterol 45: 285-290, 2010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

