Gender-Dependent Changes in Time Production Following Quadrato Motor Training in Dyslexic and Normal Readers
- PMID: 30210326
- PMCID: PMC6123388
- DOI: 10.3389/fncom.2018.00071
Gender-Dependent Changes in Time Production Following Quadrato Motor Training in Dyslexic and Normal Readers
Abstract
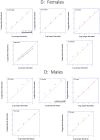
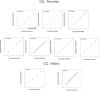
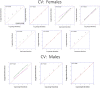
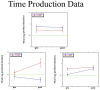
Time estimation is an important component of the ability to organize and plan sequences of actions as well as cognitive functions, both of which are known to be altered in dyslexia. While attention deficits are accompanied by short Time Productions (TPs), expert meditators have been reported to produce longer durations, and this seems to be related to their increased attentional resources. In the current study, we examined the effects of a month of Quadrato Motor Training (QMT), which is a structured sensorimotor training program that involves sequencing of motor responses based on verbal commands, on TP using a pre-post design. QMT has previously been found to enhance attention and EEG oscillatory activity, especially within the alpha range. For the current study, 29 adult Hebrew readers were recruited, of whom 10 dyslexic participants performed the QMT. The normal readers were randomly assigned to QMT (n = 9) or Verbal Training (VT, identical cognitive training with no overt motor component, and only verbal response, n = 10). Our results demonstrate that in contrast to the controls, longer TP in females was found following 1 month of intensive QMT in the dyslexic group, while the opposite trend occurred in control females. We suggest that this longer TP in the female dyslexics is related to their enhanced attention resulting from QMT. The current findings suggest that the combination of motor and mindful training, embedded in QMT, has a differential effect depending on gender and whether one is dyslexic or not. These results have implications for educational and contemplative neuroscience, emphasizing the connection between specifically-structured motor training, time estimation and attention.
Keywords: dyslexia; gender difference; quadrato motor training; time and motion studies; time production.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Scoping Review on Movement, Neurobiology and Functional Deficits in Dyslexia: Suggestions for a Three-Fold Integrated Perspective.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 14;20(4):3315. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20043315. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36834011 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in cerebellar activity and inter-hemispheric coherence accompany improved reading performance following Quadrato Motor Training.Front Syst Neurosci. 2014 May 9;8:81. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2014.00081. eCollection 2014. Front Syst Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24847224 Free PMC article.
-
Embodied cognitive flexibility and neuroplasticity following Quadrato Motor Training.Front Psychol. 2015 Jul 22;6:1021. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01021. eCollection 2015. Front Psychol. 2015. PMID: 26257679 Free PMC article.
-
A suspended act: increased reflectivity and gender-dependent electrophysiological change following Quadrato Motor Training.Front Psychol. 2014 Feb 3;5:55. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00055. eCollection 2014. Front Psychol. 2014. PMID: 24550872 Free PMC article.
-
The Implications of Motor and Cognitive Inhibition for Hot and Cool Executive Functions: The Case of Quadrato Motor Training.Front Psychol. 2020 May 19;11:940. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00940. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32508720 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Three-Fold Integrated Perspective on Healthy Development: An Opinion Paper.Brain Sci. 2023 May 25;13(6):857. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13060857. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37371337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The application of computerized quadrato motor training in enhancing balance and executive performance in stroke patients.Sci Rep. 2025 May 29;15(1):18850. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02145-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40442149 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Creating an Internal Environment of Cognitive and Psycho-Emotional Well-Being through an External Movement-Based Environment: An Overview of Quadrato Motor Training.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Jun 18;16(12):2160. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16122160. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31216778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Scoping Review on Movement, Neurobiology and Functional Deficits in Dyslexia: Suggestions for a Three-Fold Integrated Perspective.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 14;20(4):3315. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20043315. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36834011 Free PMC article.
-
Change in Time Perception Following the Place of Pre-Existence Technique.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 16;20(4):3509. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20043509. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36834202 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ben-Soussan T. D., Avirame K., Glicksohn J., Goldstein A., Harpaz Y., Ben-Schachar M. (2014a). Changes in cerebellar activity and inter-hemispheric coherence accompany improved reading capacity following Quadrato Motor Training. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 8:81. 10.3389/fnsys.2014.00081 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

