Correlation analysis of intestinal flora with hypertension
- PMID: 30210587
- PMCID: PMC6122545
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6500
Correlation analysis of intestinal flora with hypertension
Abstract
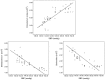
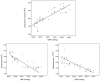
Relationship between intestinal flora content and hypertension was investigated. Ninety-four patients with hypertension who were admitted and treated in No. 215 Hospital of Shaanxi Nuclear Industry from May 2016 to April 2017 were selected as the observation group; and 94 healthy people from the physical examination center of No. 215 Hospital of Shaanxi Nuclear Industry in the same time period were selected as the control group. The systolic (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) of all the participants were measured. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to detect the quantities of Eubacterium rectale, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron and Bifidobacterium in the intestines, and correlation analyses were performed. The SBP, DBP and content of Eubacterium rectale in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group, while the contents of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron and Bifidobacterium were obviously lower than those in the control group (P<0.05). Pearson's correlation analysis showed that Eubacterium rectale was positively correlated with SBP and DBP, while Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron and Bifidobacterium had a negative correlation with SBP and DBP (P<0.05). The results showed that the quantities of Bifidobacterium and Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron are decreased while the number of Eubacterium rectale is increased in the intestines of patients with hypertension. Moreover, the content of intestinal flora has a significant correlation with hypertension.
Keywords: correlation; hypertension; intestinal flora.
Figures
References
-
- Matsumura K, Arima H, Tominaga M, Ohtsubo T, Sasaguri T, Fujii K, Fukuhara M, Uezono K, Morinaga Y, Ohta Y, et al. COMFORT Investigators Effect of losartan on serum uric acid in hypertension treated with a diuretic: The COMFORT study. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2015;37:192–196. doi: 10.3109/10641963.2014.933968. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
