Mandible exosomal ssc-mir-133b regulates tooth development in miniature swine via endogenous apoptosis
- PMID: 30210900
- PMCID: PMC6131536
- DOI: 10.1038/s41413-018-0028-5
Mandible exosomal ssc-mir-133b regulates tooth development in miniature swine via endogenous apoptosis
Abstract
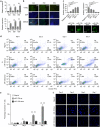
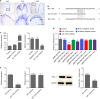
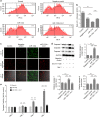
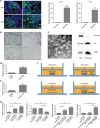
Signal transduction between different organs is crucial in the normal development of the human body. As an important medium for signal communication, exosomes can transfer important information, such as microRNAs (miRNAs), from donors to receptors. MiRNAs are known to fine-tune a variety of biological processes, including maxillofacial development; however, the underlying mechanism remains largely unknown. In the present study, transient apoptosis was found to be due to the expression of a miniature swine maxillofacial-specific miRNA, ssc-mir-133b. Upregulation of ssc-mir-133b resulted in robust apoptosis in primary dental mesenchymal cells in the maxillofacial region. Cell leukemia myeloid 1 (Mcl-1) was verified as the functional target, which triggered further downstream activation of endogenous mitochondria-related apoptotic processes during tooth development. More importantly, mandible exosomes were responsible for the initial apoptosis signal. An animal study demonstrated that ectopic expression of ssc-mir-133b resulted in failed tooth formation after 12 weeks of subcutaneous transplantation in nude mice. The tooth germ developed abnormally without the indispensable exosomal signals from the mandible.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Commentary on "Mandible exosomal ssc-mir-133b regulates tooth development in miniature swine via endogenous apoptosis".Bone Res. 2018 Oct 17;6:29. doi: 10.1038/s41413-018-0033-8. eCollection 2018. Bone Res. 2018. PMID: 30345150 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Identification of differential microRNA expression during tooth morphogenesis in the heterodont dentition of miniature pigs, SusScrofa.BMC Dev Biol. 2015 Dec 29;15:51. doi: 10.1186/s12861-015-0099-0. BMC Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26715101 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-133b suppresses glioma progression via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by targeting EZH2.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Dec 16;10(1):381. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1446-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31842978 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Exosomes Derived from miR-133b Modified MSCs in an Experimental Rat Model of Intracerebral Hemorrhage.J Mol Neurosci. 2018 Mar;64(3):421-430. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1041-2. Epub 2018 Feb 17. J Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29455449
-
Exosomal microRNA communication between tissues during organogenesis.RNA Biol. 2017 Dec 2;14(12):1683-1689. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1361098. Epub 2017 Sep 29. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 28816640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Cell Death in Cellular Processes During Odontogenesis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 18;9:671475. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.671475. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34222243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mandible-derived extracellular vesicles regulate early tooth development in miniature swine via targeting KDM2B.Int J Oral Sci. 2025 Apr 27;17(1):36. doi: 10.1038/s41368-025-00348-w. Int J Oral Sci. 2025. PMID: 40289114 Free PMC article.
-
Complement 3 mediates periodontal destruction in patients with type 2 diabetes by regulating macrophage polarization in periodontal tissues.Cell Prolif. 2020 Oct;53(10):e12886. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12886. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 32794619 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Alzheimer's disease with framework nucleic acids.Cell Prolif. 2020 Apr;53(4):e12787. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12787. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 32162733 Free PMC article.
-
Controlled release of odontogenic exosomes from a biodegradable vehicle mediates dentinogenesis as a novel biomimetic pulp capping therapy.J Control Release. 2020 Aug 10;324:679-694. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.06.006. Epub 2020 Jun 10. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32534011 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

